The PICTURE clause describes the general characteristics and editing requirements of an elementary item.
General Format

Directives
- In addition to Compiler directives which provide flagging and modify the reserved word list, the following directive may impact either the syntax or the semantics described in this section.
General Rules
The categories of data that can be described with a PICTURE clause are: alphabetic, numeric, alphanumeric, alphanumeric edited, numeric edited,

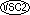
 external floating-point,
external floating-point,
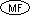
 and boolean.
and boolean.
General rules within these categories are given below:
Alphabetic Data Rules
- The PICTURE character-string can contain only the symbols "A" and "B".
 The PICTURE character-string can contain only the symbol "A".
The PICTURE character-string can contain only the symbol "A".
- The contents when represented in standard data format must be one or more alphabetic characters.
Numeric Data Rules
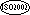
- The PICTURE character-string can contain only the symbols "9", "P", "S", and "V". The number of digit positions that can be described by the PICTURE character-string must range from 1 through 18.

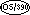 The PICTURE character-string can contain up to 31 digit positions.
The PICTURE character-string can contain up to 31 digit positions.
 The PICTURE character-string can contain up to 18 digit positions by default or if you set INTLEVEL"2", and up to 38 digit positions if you set INTLEVEL"4".
The PICTURE character-string can contain up to 18 digit positions by default or if you set INTLEVEL"2", and up to 38 digit positions if you set INTLEVEL"4".
- If unsigned, the data in standard data format must be a combination of the Arabic numerals "0", "1", "2", " 3", "4", "5", "6", "7", "8", and "9"; if signed, the item can also contain a "+", "-", or other representation of an operational sign. (See the topic
The SIGN Clause.)
Alphanumeric Data Rules
- The PICTURE character-string is restricted to certain combinations of the symbols " A", "X", "9", and the item is treated as if the character-string contained all X"s. A PICTURE character-string which contains all A"s or all 9"s does not define an alphanumeric item.
- The contents when represented in standard data format can consist of any characters in the computer's character set.
Alphanumeric Edited Data Rules
- The PICTURE character-string is restricted to certain combinations of the following symbols: "A", "X", " 9", "B", "0", and "/" as follows:
- The character-string must contain at least one "B" and at least one "X" or at least one "0" (zero) and at least one "X" or at least one "/" (slash) and at least one "X", or:
- The character-string must contain at least one "0" (zero) and at least one "A" or at least one "/" (slash) and at least one "A".
- The contents when represented in standard data format can consist of any characters in the computer's character set.
Numeric Edited Data Rules
- The PICTURE character-string is restricted to certain combinations of the symbols "B", "/", "P", "V" , "Z", "0", "9", ",", ".", "*", "+", "-", "CR", "DB", and the currency symbol. The allowable combinations are determined from the order of precedence of symbols and the editing rules as follows:
- The number of digit positions that can be represented in the PICTURE character-string must range from 1 through 18.

 The PICTURE character-string can contain up to 31 digit positions.
The PICTURE character-string can contain up to 31 digit positions.
 The PICTURE character-string can contain up to 18 digit positions by default or if you set INTLEVEL"2", and up to 38 digit positions if you set INTLEVEL"4".
The PICTURE character-string can contain up to 18 digit positions by default or if you set INTLEVEL"2", and up to 38 digit positions if you set INTLEVEL"4".
- The character-string must contain at least one "0" , "B", "/", "Z", "*", "+", ",", ".", "-", "CR" , "DB", or currency symbol.
- The contents of the character positions that represent a digit must be one of the numerals.
- If all character positions in the PICTURE character-string are represented by an insertion character, at least one of the insertion characters must be positioned to the left of the decimal point.


External Floating-point Data Items
- The PICTURE string must have the following form:

A sign character must immediately precede both the significand and the exponent.
A "+" sign indicates that a positive sign will be used in the output to represent positive values and that a negative sign will represent negative values.
A "-"sign indicates that a blank will be used in the output to represent positive values and that a negative sign will represent negative values.
Each sign position occupies one byte of storage.
significand
The significand can contain the symbols:
9 . V
An actual decimal point can be represented with a period while an assumed decimal point is represented by a V. Either an actual or an assumed decimal point must be present in the significand; the decimal point can be leading, embedded or trailing. The significand can contain from 1 to 16 numeric characters.
E
Indicates the exponent.
exponent
The exponent must be a PIC "99".
- The OCCURS, REDEFINES and RENAMES clauses can be associated with external floating-point items.
- The SIGN clause is documentary only and has no effect on the representation of the sign.
- The SYNCHRONIZED clause is documentary only.
- The following clauses are invalid with external floating-point items:
BLANK WHEN ZERO JUSTIFIED VALUE
Boolean Data Rules
- The PICTURE character-string can contain only the symbol "1".
- The PICTURE character-string can contain up to 64 digit positions.
- Values can be specified in literals with an opening separator B", for example B"1110", where the value is expressed as bits.






![]()
![]()
![]() The maximum number of characters allowed in the character-string is 50.
The maximum number of characters allowed in the character-string is 50.
![]() This construct is, however, permitted, in which case zero suppression overrides the BLANK WHEN ZERO clause.
This construct is, however, permitted, in which case zero suppression overrides the BLANK WHEN ZERO clause.
![]()
![]()
![]() external floating-point,
external floating-point,
![]()
![]() and boolean.
and boolean.
![]()
![]() The PICTURE character-string can contain up to 31 digit positions.
The PICTURE character-string can contain up to 31 digit positions.
![]() The PICTURE character-string can contain up to 18 digit positions by default or if you set INTLEVEL"2", and up to 38 digit positions if you set INTLEVEL"4".
The PICTURE character-string can contain up to 18 digit positions by default or if you set INTLEVEL"2", and up to 38 digit positions if you set INTLEVEL"4".
![]()
![]() The PICTURE character-string can contain up to 31 digit positions.
The PICTURE character-string can contain up to 31 digit positions.
![]() The PICTURE character-string can contain up to 18 digit positions by default or if you set INTLEVEL"2", and up to 38 digit positions if you set INTLEVEL"4".
The PICTURE character-string can contain up to 18 digit positions by default or if you set INTLEVEL"2", and up to 38 digit positions if you set INTLEVEL"4".



Comments:
The size of an elementary item, where size means the number of character positions occupied by the elementary item in standard data format, is determined by the number of allowable symbols that represent character positions. An integer which is enclosed in parentheses following the symbols "A", ",", "X" , "9", "P", "Z", "*", "B", "/", "0", "+", "-", or the currency symbol indicates the number of replications of the symbol. Note that the following symbols can appear only once in a given PICTURE: "S" , "V", ".", "CR", and "DB",
The functions of the symbols used to describe an elementary item are explained as follows:
The character "P" and the insertion character "." (period) cannot both occur in the same PICTURE character-string. If, in any operation involving conversion of data from one form of internal representation to another, the data item being converted is described with the PICTURE character "P", each digit position described by a "P" is considered to contain the value zero, and the size of the data item is considered to include the digit positions so described.
The first occurrence of the currency symbol adds the number of characters in the currency string to the size of the item. Each subsequent occurrence of the currency symbol adds one to the size of the item.
The CURRENCY Compiler directive also affects the currency symbol used.
Two general methods of performing editing in the PICTURE clause are available: insertion or suppression and replacement. Four types of insertion editing are available:
Two types of suppression and replacement editing are available:
The type of editing which can be performed upon an item is dependent upon the category to which the item belongs. The table below specifies which type of editing can be performed upon a given category.
The "," (comma), "B" (space), "0" (zero), and " /" (slash) are used as the insertion characters. The insertion characters are counted in the size of the item and represent the position in the item into which the character will be inserted.
The "." (period) is used as the insertion character. In addition to being an insertion character it represents the decimal point for alignment purposes. The insertion character used for the actual decimal point is counted in the size of the item. The use of the assumed decimal point, represented by the symbol "V" and the actual decimal point, represented by the insertion character, in the same PICTURE character-string is disallowed. The result of special insertion editing is the appearance of the insertion character in the item in the same position as shown in the character-string.
The currency string and the editing sign control symbols "+" , "-", "CR", "DB" are the insertion characters. Only one currency symbol and only one of the editing sign control symbols can be used in a given PICTURE character-string. When the symbols "CR" or "DB" are used, they represent two character positions in determining the size of the item and they must represent the rightmost character positions that are counted in the size of the item. The symbol "+" or "-", when used, must be either the leftmost or rightmost character position to be counted in the size of the item. The currency symbol must be the leftmost character.
The currency symbol and the editing sign control symbols "+" and "-" are the floating insertion symbols and as such are mutually exclusive in a given PICTURE character-string.
Floating insertion editing is indicated in a PICTURE character-string by using a string of at least two of the floating insertion symbols. This string of floating insertion characters can contain any of the simple insertion characters or have simple insertion characters immediately to the right of this string. These simple insertion characters are part of the floating string.
When the floating insertion character is the currency symbol, this string of floating insertion characters can have one of the editing sign control symbols "+", "-", "CR" or " DB" immediately to the right of this string.
The leftmost character of the floating insertion string represents the leftmost limit of the floating symbol in the data item. The rightmost character of the floating string represents the rightmost limit of the floating symbols in the data item.
The second floating character from the left represents the leftmost limit of the numeric data that can be stored in the data item. Non-zero numeric data can replace all the characters at or to the right of this limit.
Floating insertion editing can be represented in a PICTURE character-string in only two ways. One way is to represent any or all of the leading numeric character positions on the left of the decimal point by the insertion character. The other way is to represent all of the numeric character positions in the PICTURE character-string by the insertion character.
If the insertion characters are only to the left of the decimal point in the PICTURE character-string, the result is that a single floating insertion character will be placed into the character position immediately preceding either the decimal point or the first non-zero digit in the data represented by the insertion symbol string, whichever is farther to the left in the PICTURE character-string. The character positions preceding the insertion character are replaced with spaces.
If all numeric character positions in the PICTURE character-string are represented by the insertion character, the result depends upon the value of the data. If the value is zero, the entire data item will contain spaces. If the value is not zero, the result is the same as when the insertion character is only to the left of the decimal point.
To avoid truncation, the minimum size of the PICTURE character-string for the receiving data item must be the number of characters in the sending data item, plus the number of non-floating insertion characters being edited into the receiving data item, plus one for the floating insertion character.
The suppression of leading zeros in numeric character positions is indicated by the use of the alphabetic character "Z" or the character "*" (asterisk) as suppression symbols in a PICTURE character-string. These symbols are mutually exclusive in a given PICTURE character-string. Each suppression symbol is counted in determining the size of the item. If "Z" is used, the replacement character will be the space and if the asterisk is used, the replacement character will be "*".
Zero suppression and replacement is indicated in a PICTURE character-string by using a string of one or more of the allowable symbols to represent leading numeric character positions which are to be replaced when the associated character position in the data contains a zero. Any of the simple insertion characters embedded in the string of symbols or to the immediate right of this string are part of the string.
Zero suppression can be represented in a PICTURE character-string in only two ways. One way is to represent any or all of the leading numeric character positions to the left of the decimal point by suppression symbols. The other way is to represent all of the numeric character positions in the PICTURE character-string by suppression symbols.
If the suppression symbols appear only to the left of the decimal point, any leading zero in the data which corresponds to a symbol in the string is replaced by the replacement character. Suppression terminates at the first non-zero digit in the data represented by the suppression symbol string or at the decimal point, whichever is encountered first.
If all numeric character positions in the PICTURE character-string are represented by suppression symbols and the value of the data is not zero, the result is the same as if the suppression characters were only to the left of the decimal point. If the value is zero and the suppression symbol is "Z", the entire data item will be spaces. If the value is zero and the suppression symbol is "*", the data item will be all "*" except for the actual decimal point.
The symbols "+", "-", "*", " Z" and the currency symbol, when used as floating replacement characters, are mutually exclusive within a given character-string.
The table below shows the order of precedence when using characters as symbols in a character-string. An "X" at an intersection indicates that the symbol(s) at the top of the column can precede, in a given character-string, the symbol(s) at the left of the row. Arguments appearing in braces indicate that the symbols are mutually exclusive. The currency symbol is indicated by the symbol "cs". At least one of the symbols "A " , "X", "Z", " 9" or "*", or at least two of the symbols "+" , "-" or "cs" must be present in a PICTURE string.
In this table, non-floating insertion symbols "+" and "-" , floating insertion symbols "Z", "*", " +", "-", and "cs", and other symbol "P" appear twice in the PICTURE character precedence chart. The leftmost column and uppermost row for each symbol represents its use to the left of the decimal point position. The second appearance of symbol in the row and column represents its use to the right of the decimal point position.