9.1 About Planning Objects
Because your production environment is complex and changeable, an IT transformation project can take months, or even years, to complete. PlateSpin Transformation Manager supports rolling wave planning to accommodate the near-term and long-term planning of your transformation tasks.
PTM is designed to handle hundreds to tens of thousands of workloads per project. Within each project, you can schedule the transformations to occur in waves with smaller groupings of batches in each wave.
Figure 9-1 shows the parent-child relationships between planning objects: Organizations, Projects, Waves, Batches, and Workloads.
Figure 9-1 Parent-Child Relationships of Planning Objects
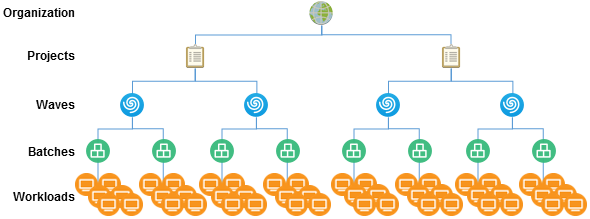
9.1.1 Organizations

An organization in PlateSpin Transformation represents a business organization or tenant that consumes the PTM services. PTM provides logical secure segregation of data for each organization.
9.1.2 Projects

Each organization in PlateSpin Transformation Manager can have one or more projects. The scope and purpose for each project depends on your business needs and migration goals. PTM provides logical secure segregation of data for each project.
9.1.3 Waves

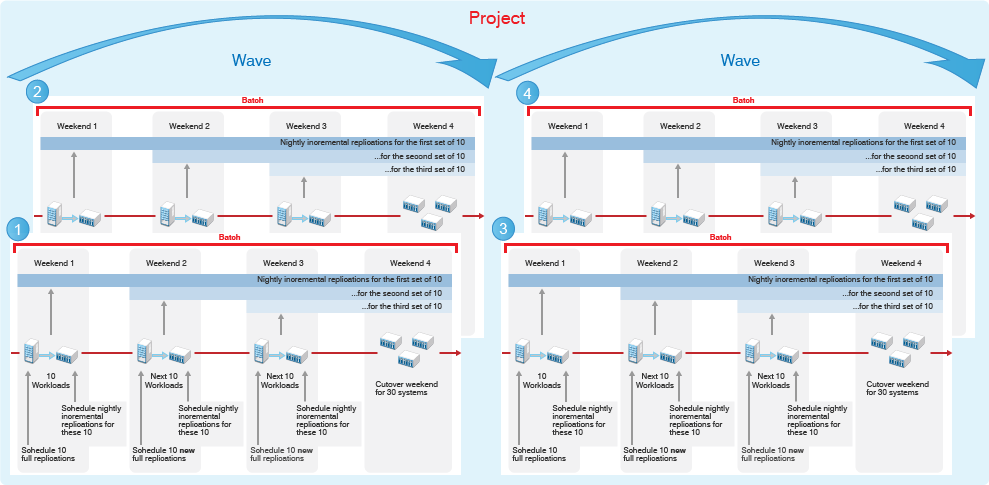
You can organize the project’s transformation tasks in waves, as shown in Figure 9-2. For near-term waves, you can plan the tasks in detail. You can refine the transformation plan for future waves as newer and better information becomes available.
Figure 9-2 Wave Planning
9.1.4 Batches

Within a wave, batches group like workloads that you want to transform together. Batches can be more easily scheduled during intervals when Network resources are available. You can deliver valuable results in each batch and wave. Schedules are flexible. You can coordinate the start dates and cutover dates with stakeholders to work around planned events that are critical to the business.
Figure 9-3 Batch Planning

9.1.5 Applications

Applications represent the business purpose of workloads based on the software installed on them. They are defined at the project level, then associated as attributes of source workloads. Application information can help you identify workloads with interdependent or mutually exclusive relationships as you organize workloads for migration.
9.1.6 Workloads

Transforming workloads from their current operational mode to a future operational mode is the fundamental management goal for your transformation project. PlateSpin Transformation Manager helps you plan three types of transformation: automated, manual, and decommission. See Table 9-1 for a description of each transformation type.
Table 9-1 Transformation Planning
|
Transformation Type |
Description |
|---|---|
|
Automated |
You import workloads and configure a custom transformation plan for each workload based on the target platform. PTM controls the migration workflow based on the migration preferences. |
|
Manual or Manual (Tracking) |
You import workloads and configure a basic transformation plan for each workload. For manual migrations, you manually enter the migration status changes for the imported workloads as migration tasks are completed. For manual migrations with tracking, you perform the external migrations using your PlateSpin Migrate servers. PTM automatically gets the migration status from the Migrate server as migration tasks are completed. |
|
Decommission |
You import workloads and configure a basic transformation plan for each workload. You manually enter the status changes as tasks are completed for decommission. |