13.3 Configuring a PlateSpin User with Minimal Permissions on VMware
PlateSpin Migrate does not require administrative access to a VMware environment to perform workload migrations. Migrate requires permissions only for the VMware resources it must access to execute tasks in the migration workflow and functions.
To establish minimal permissions for a Migrate Server in a target VMware environment:
-
Create a special-purpose PlateSpin user to represent the Migrate server.
-
In vSphere, create predefined PlateSpin roles, and configure each role with the predefined minimum required VMware privileges.
-
Assign to the PlateSpin user an appropriate role for each type of VMware resource that you want Migrate to be able to access for migration to the VMware environment.
Review the information in this section to understand the PlateSpin roles for VMware and how to assign them in your VMware environment.
13.3.1 About PlateSpin VMware Roles and Permissions
PlateSpin Migrate provides custom VMware roles that you can use to control access for Migrate in your VMware environment. Each role is a set of predefined minimal permissions needed to perform actions in the migration workflow. For each Migrate server, you create a special-purpose PlateSpin user that represents the Migrate server in vCenter. To permit required actions, you associate the PlateSpin user with the appropriate role on various VMware resources that Migrate needs to access.
The PlateSpinRole.xml file on the Migrate server defines the minimum required privileges for each role. After you associate the roles for a special PlateSpin user, PlateSpin Migrate will have all the necessary VMware permissions to complete a migration.
-
PlateSpin Virtual Infrastructure Manager
-
PlateSpin Virtual Machine Manager
-
PlateSpin User
For more granular control, you can establish the following four roles for a PlateSpin user to filter out resources for which the user does not have sufficient privileges to perform migrations. Use equivalent roles to more narrowly apply permissions to different VMware resource types. The PlateSpin VMware Role Tool cannot create these roles for you.
-
PlateSpin Datastore Manager
-
PlateSpin Network Manager
-
PlateSpin Cluster Manager
-
PlateSpin Virtual Machine User
For your convenience, PlateSpin Migrate provides the PlateSpin VMware Role Tool and role definitions that you can use to configure the required PlateSpin roles and permissions in your VMware environment. Table 13-1 describes these resources, which are available in the <Migrate-install-folder>\PlateSpin Migrate Server\bin\VMwareRolesTool directory.
Table 13-1 Migrate Resources for Setting VMware Roles and Permissions
|
File Name |
Description |
|---|---|
|
PlateSpinRole.xml |
The PlateSpin Role XML file defines VMware custom roles and the minimum required VMware privileges for each role. |
|
PlateSpin.VMwareRoleTool.exe |
PlateSpin VMware Role Tool creates certain VMware roles in a VMware environment and automatically sets the minimum privileges for them. |
13.3.2 Assigning VMware Roles in a Single User Environment
To grant permissions for the PlateSpin user in a single-user environment, you assign the appropriate role for the PlateSpin user for a specific vCenter inventory object. The user can have different roles for different objects.
About Role Assignments in a Single-User Environment
As you set up a single-user environment, you create a PlateSpin user to represent the Migrate server in the VMware environment. You assign the PlateSpin VMware roles to the user for the VMware resources, according to the resources that user must be able to access, and only those resources. In the VMware environment, it is this PlateSpin user that creates the Migrate target and performs actions on it during the migration.
Table 13-2 describes the role assignments across your VMware environment that are required to perform a migration. Assign the roles to the PlateSpin user for the VMware resources that you want the Migrate Server to access. Ensure that you do not extend permissions to the PlateSpin user for resources that you do not want the Migrate Server to access.
IMPORTANT:Propagating any permission has security implications. For security reasons, propagating privileges is not recommended for role assignments at the root of the Inventory tree and for DataCenter objects. Otherwise, propagation settings are at the discretion of the VMware administrator, except as noted.
Table 13-2 PlateSpin User: Role Assignments for VMware Resource Types
|
PlateSpin Role (or Equivalent Custom Role) |
Propagation Instructions |
More information |
|---|---|---|
|
Root of the vCenter Inventory tree |
||
|
PlateSpin Virtual Infrastructure Manager |
Non-propagation recommended |
This setting enables Migrate to monitor tasks being performed by Migrate software and to end any stale VMware sessions. |
|
Each DataCenter object that contains target clusters and hosts |
||
|
PlateSpin Virtual Infrastructure Manager |
Non-propagation recommended |
This setting enables Migrate to access the data center’s datastores for file upload and download. |
|
Target cluster and its member hosts |
||
|
PlateSpin Virtual Infrastructure Manager |
You can propagate permission from the Cluster object to Host objects, or create an additional permission on each of its member Host objects. If you assign the role on the cluster object and propagate it, no further changes are necessary when you add a new host to the cluster. However, propagating this permission has security implications. |
Configure the role on each target cluster (and its member hosts) that you will specify as a migration target. |
|
Resource pool |
||
|
PlateSpin Virtual Machine Manager |
Configure the PlateSpin Virtual Machine Manager role on at least one resource pool. You can grant permissions to one or multiple resource pools that are available to the enabled clusters. |
|
|
PlateSpin Virtual Machine User |
(Optional) Configure the PlateSpin Virtual Machine User role on resource pools you want to filter out. |
|
|
VM folder |
||
|
PlateSpin Virtual Machine Manager |
Configure the PlateSpin Virtual Machine Manager role on at least one VM folder. You can grant permissions to one or multiple VM folders. |
|
|
PlateSpin Virtual Machine User |
(Optional) Configure the PlateSpin Virtual Machine User role on VM folders you want to filter out. |
|
|
Network (dvSwitch or vNet) |
||
|
PlateSpin Virtual Machine Manager |
To assign the correct role to a dvSwitch, propagate the role on the data center (resulting in an additional object receiving the role), or place the dvSwitch in a folder and assign the role on that folder. |
Configure the PlateSpin Virtual Machine Manager role on at least one Network. You can grant permissions to one or multiple networks that are available to the enabled clusters. For a standard portgroup to be listed as an available network in the Migrate UI, create a definition for it on every host in the cluster. |
|
PlateSpin Network Manager |
|
(Optional) Configure the Network Manager role on networks you want to filter out. For a standard portgroup to be listed as an available network in the Migrate UI, create a definition for it on every host in the cluster. |
|
Datastore / Datastore cluster |
||
|
PlateSpin Virtual Machine Manager |
For Datastore Clusters, the permission must be propagated to the contained datastores. Not providing access to an individual member of the cluster causes both Prepare and Full Replication to fail. |
Configure the PlateSpin Virtual Machine Manager role on at least one datastore or datastore cluster. You can grant permissions to one or multiple datastores or datastore clusters that are available to the enabled clusters. |
|
PlateSpin Datastore Manager |
|
(Optional) Configure the PlateSpin Datastore Manager role on datastores or datastore clusters you want to filter out. |
Security Implications of Assigning VMware Roles
When you assign VMware roles to the PlateSpin user, the key security implications include:
-
With the PlateSpin Virtual Infrastructure Manager role assigned to the vCenter object, the PlateSpin user can see (but not affect) the tasks performed by every other user.
-
Because there is no way to set permissions on datastore folders and subfolders, the PlateSpin user with permissions on a datastore has access to all disks stored on that datastore.
-
With the PlateSpin Virtual Infrastructure Manager role assigned to a Cluster object, the PlateSpin user is able to turn off/on HA or DRS on the entire cluster.
-
Setting the PlateSpin Virtual Infrastructure Manager role on the DRS Cluster object and propagating this role allows the PlateSpin user to see all VMs placed in the default resource pool and/or default VM folder. Also, propagation requires the administrator to explicitly set the PlateSpin user to have a “No Access” role on every resource pool and VM folder that the user should not be able to access.
-
Setting the PlateSpin Virtual Infrastructure Manager role on the vCenter object allows the PlateSpin user to end sessions of any other user connected to the vCenter.
13.3.3 Assigning VMware Roles in a Multitenancy Environment
In a multitenancy environment, the custom VMware roles for PlateSpin makes it possible for you, as a service provider, to segment your VMware cluster to allow multitenancy: where multiple Migrate targets are instantiated in your data center to accommodate Migrate customers or “tenants” who want to keep their data and evidence of their existence separate from and inaccessible to other customers who also use your data center.
About Role Assignments in a Multitenancy Environment
As you set up a multitenancy environment, you need to provision a single Migrate server per customer or “tenant.” For each tenant, you create a PlateSpin user to represent that tenant’s Migrate server in the VMware environment. You assign the PlateSpin VMware roles to the user for the VMware resources, according to the resources that user must be able to access, and only those resources. In the VMware environment, it is the tenant-based PlateSpin user that creates the Migrate target and performs actions on it during the migration. As service provider, you maintain this user’s credentials and do not disclose them to your tenant customer.
Table 13-3 describes the role assignments across your VMware environment that are required to perform a migration. Assign the roles to each of the tenant-based PlateSpin users for the VMware resources that you want the tenant’s Migrate Server to access. Ensure that you do not extend permissions to the tenant-based PlateSpin user for the tenant’s resources that you do not want the Migrate Server to access.
IMPORTANT:Propagating any permission has security implications. For security reasons, propagating privileges is not recommended for role assignments at the root of the Inventory tree and for DataCenter objects. Otherwise, propagation settings are at the discretion of the VMware administrator, except as noted.
Table 13-3 Tenant-Based PlateSpin User: Role Assignments for the Tenant’s VMware Resource Types
|
PlateSpin Role |
Propagation Instructions |
More information |
|---|---|---|
|
Root of the vCenter Inventory tree |
||
|
PlateSpin Virtual Infrastructure Manager |
Non-propagation recommended |
This setting enables Migrate to monitor tasks being performed by Migrate software and to end any stale VMware sessions. |
|
Each DataCenter object that contains target clusters and hosts |
||
|
PlateSpin Virtual Infrastructure Manager |
Non-propagation recommended |
This setting enables Migrate to access the data center’s datastores for file upload and download. |
|
Target cluster and its member hosts |
||
|
PlateSpin Virtual Infrastructure Manager |
You can propagate permission from the Cluster object to Host objects, or create an additional permission on each of its member Host objects. If you assign the role on the cluster object and propagate it, no further changes are necessary when you add a new host to the cluster. However, propagating this permission has security implications. |
Configure the role on each target cluster (and its member hosts) that you will specify as a migration target. |
|
Resource pool |
||
|
PlateSpin Virtual Machine Manager |
Configure the PlateSpin Virtual Machine Manager role on at least one resource pool. You can grant permissions to one or multiple resource pools that are available to the enabled clusters. |
|
|
PlateSpin Virtual Machine User |
(Optional) Configure the PlateSpin Virtual Machine User role on resource pools you want to filter out. |
|
|
VM folder |
||
|
PlateSpin Virtual Machine Manager |
Configure the PlateSpin Virtual Machine Manager role on at least one VM folder. You can grant permissions to one or multiple VM folders. |
|
|
PlateSpin Virtual Machine User |
|
(Optional) Configure the PlateSpin Virtual Machine User role on VM folders you want to filter out. |
|
Network (dvSwitch or vNet) |
||
|
PlateSpin Virtual Machine Manager |
To assign the correct role to a dvSwitch, propagate the role on the data center (resulting in an additional object receiving the role), or place the dvSwitch in a folder and assign the role on that folder. |
Configure the PlateSpin Virtual Machine Manager role on at least one Network. You can grant permissions to one or multiple networks that are available to the enabled clusters. For a standard portgroup to be listed as an available network in the Migrate UI, create a definition for it on every host in the cluster. |
|
PlateSpin Network Manager |
|
(Optional) Configure the Network Manager role on networks you want to filter out. For a standard portgroup to be listed as an available network in the Migrate UI, create a definition for it on every host in the cluster. |
|
Datastore / Datastore cluster |
||
|
PlateSpin Virtual Machine Manager |
For Datastore Clusters, the permission must be propagated to the contained datastores. Not providing access to an individual member of the cluster causes both Prepare and Full Replication to fail. |
Configure the PlateSpin Virtual Machine Manager role on at least one datastore or datastore cluster. You can grant permissions to one or multiple datastores or datastore clusters that are available to the enabled clusters. |
|
PlateSpin Datastore Manager |
|
(Optional) Configure the PlateSpin Datastore Manager role on datastores or datastore clusters you want to filter out. |
Table 13-4 describes the role you can assign to the customer or tenant user.
Table 13-4 Tenant-Based PlateSpin User: Role Assignments for the Tenant User
|
PlateSpin Role |
Propagation Instructions |
More information |
|---|---|---|
|
Each Resource Pool and Folder where the tenant’s VMs will be created |
||
|
PlateSpin User role |
|
This tenant is a member of the PlateSpin Administrators group on the PlateSpin Migrate server and is also on the vCenter Server. If the tenant will be granted the ability to change the resources used by the VM (that is, networks, ISO images, and so forth), grant this user the necessary permissions on those resources. For example, if want to you allow the customer to change the network where their VM is attached, this user should be assigned the Read-only role (or better) on all of the networks being made accessible to the customer. |
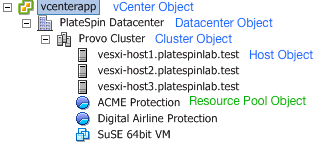
Figure 13-3 illustrates a Virtual Infrastructure in the vCenter console. The objects labeled in blue are assigned the Infrastructure Manager role. The objects labeled in green are assigned the Virtual Machine Manager role. The tree does not show VM Folders, Networks, and Datastores. Those objects are assigned the PlateSpin Virtual Machine Manager role.
Figure 13-3 Roles assigned in vCenter
Security Implications of Assigning VMware Roles in a Multitenancy Environment
PlateSpin Migrate software uses a tenant-based PlateSpin user only to perform actions in the migration workflow. From your perspective as a service provider, an end user never has access to the tenant-based PlateSpin user’s credentials and is unable to access the same set of VMware resources. In an environment where multiple Migrate servers are configured to use the same vCenter environment, Migrate prevents possibilities for cross-client access.
The major security implications include:
-
With the PlateSpin Virtual Infrastructure Manager role assigned to the vCenter object, each tenant-based PlateSpin user can see (but not affect) the tasks performed by every other user.
-
Because there is no way to set permissions on datastore folders/subfolders, each tenant-based PlateSpin user with permissions on a datastore has access to all other tenant users’ disks stored on that datastore.
-
With the PlateSpin Virtual Infrastructure Managerrole assigned to the Cluster object, each tenant-based PlateSpin user is able to turn off/on HA or DRS on the entire cluster.
-
Setting the PlateSpin Virtual Infrastructure Manager role on the DRS Cluster object and propagating this role allows the tenant-based PlateSpin user to see all VMs placed in the default resource pool and/or default VM folder. Also, propagation requires the administrator to explicitly set the tenant-based PlateSpin user to have a “no-access” role on every resource pool/VM folder that he or she should not have access to.
-
Setting the PlateSpin Virtual Infrastructure Managerrole on the vCenter object allows the enabled user to end sessions of any other user connected to the vCenter.
NOTE:Remember, in these scenarios, different tenant-based PlateSpin users are actually different instances of the PlateSpin software.
13.3.4 Configuring VMware Roles for PlateSpin Migrate
To migrate workloads to a VMware environment, PlateSpin Migrate Server must have permissions on multiple types of resources on the vCenter Server. You grant permissions to a PlateSpin user that represents the PlateSpin Server by assigning custom roles to the user on different resources.
Migrate provides information about the custom VMware roles and the minimum required privileges for each role in the <Migrate-install-folder>\PlateSpin Migrate Server\bin\VMwareRolesTool directory on your Migrate Server. For your convenience, it also provides the PlateSpin VMware Role Tool that you can use to easily create and configure the essential roles. Table 13-1 describes the files provided for this purpose.
Table 13-5 Migrate Resources for Configuring Custom VMware Roles and Permissions
|
File Name |
Description |
|---|---|
|
PlateSpinRole.xml |
The PlateSpin Role XML file defines custom VMware roles and the minimum required privileges for each role. |
|
PlateSpin.VMwareRoleTool.exe |
The PlateSpin VMware Role Tool creates essential custom VMware roles in a VMware environment and sets the minimum required privileges for each role. |
Use the information in this section to create essential custom roles on a target vCenter Server and set the minimum set of privileges for each role.
Using the PlateSpin VMware Role Tool to Define PlateSpin VMware Roles in vCenter
You can use the PlateSpin VMware Role Tool to conveniently establish the following three roles for a PlateSpin user in a VMware environment:
-
PlateSpin Virtual Machine Manager
-
PlateSpin Virtual Infrastructure Manager
-
PlateSpin User
These roles will contain all the necessary VMware permissions to complete a migration. You will assign the roles to appropriate resource types for the PlateSpin user:
This section provides usage guidelines for the PlateSpin VMware Role Tool.
Location
The PlateSpin VMware Role Tool (PlateSpin.VMwareRoleTool.exe file) is available in the <Migrate-install-folder>\PlateSpin Migrate Server\bin\VMwareRolesTool directory on the PlateSpin Migrate Server.
Syntax
From the location where the role tool is installed, run the tool from the command line, using this basic syntax:
PlateSpin.VMwareRoleTool.exe /host=<hostname-or-IP-address> /user=<vCenter-admin-user-name> /role=<the role definition file name and location> /create
Parameters
- /host=<hostname-or-IP-address>
-
Specifies the host name or IP address of the vCenter Server where the custom roles will be created or updated.
- /user=<vCenter-admin-user-name>
-
Specifies the user name of an administrator account on the vCenter Server.
- /role=<the role definition file name and location>
-
Specifies the file name of the file that defines the custom roles and their required minimum privileges. Use the PlateSpinRole.xml file unless you are advised to use a different file.
- /help
-
Displays information about parameters, actions, and optional flags.
Actions
Apply the following action parameters as needed when you use PlateSpin.VMwareRoleTool.exe to create or update custom roles in vCenter.
- /create
-
(Mandatory) Creates the roles defined by the file you specified for the /role parameter.
The default roles defined in the PlateSpinRole.xml file are:
-
PlateSpin Virtual Machine Manager role
-
PlateSpin Virtual Infrastructure Manager role
-
PlateSpin User role
-
- /get_all_privileges
-
Display all server-defined privileges.
- /get_compatible_roles
-
Display all roles that are compatible to the role defined by /role.
- /check_role=<role name>
-
Check the given role for compatibility with the role defined by /role.
Options
Apply the following optional flags as needed when you use PlateSpin.VMwareRoleTool.exe to create or update custom roles in vCenter.
- /interactive
-
Run the tool with interactive options that allow you to choose to create individual roles, check role compatibility, or list all compatible roles.
For information about using the tool in interactive mode, see VMware Role Tool to Verify Permissions to the Roles (KB 7018547).
- /password=<password>
-
Provide the VMware password (bypasses the password prompt).
- /verbose
-
Display detailed information.
Tool Usage Example
Usage:
PlateSpin.VMwareRoleTool.exe /host=houston_sales /user=pedrom /role=PlateSpinRole.xml /create
Resulting Actions:
-
The PlateSpin VMware Role Tool runs on the houston_sales vCenter Server, which has an administrator with the user name pedrom.
-
In the absence of the /password parameter, the tool prompts for the user password, which you enter.
-
The tool accesses the role definition file, PlateSpinRole.xml, which is located in the same directory as the tool executable (there was no need to further define its path).
-
The tool locates the definition file and is instructed (/create) to create the roles defined in the contents of that file in the vCenter environment.
-
The tool accesses the definition file and creates the new roles (including the appropriate minimum privileges for defined, limited access) inside vCenter.
You will later assign the roles to appropriate resource types for the PlateSpin user:
Additional Information
For information about using the tool, see VMware Role Tool to Verify Permissions to the Roles (KB 7018547).
(Optional) Manually Defining the PlateSpin Roles in vCenter
You can use the vCenter client to manually create and assign the PlateSpin custom roles. This requires creating the roles with the enumerated privileges as defined in PlateSpinRole.xml. When you manually create roles:
-
You can use the PlateSpin-defined names or custom names for the roles.
-
Each role must have the required appropriate minimum privileges from the PlateSpin definition file.
For more information about how to create custom roles in vCenter, see Using Roles to Assign Privileges in the VMware vSphere 6.7 Documentation.
Using vCenter to View Privileges for PlateSpin Custom Roles
You use the vCenter client to view the minimal privileges set for the PlateSpin custom roles.
-
In vCenter, select a custom role:
-
PlateSpin Virtual Machine Manager
-
PlateSpin Virtual Infrastructure Manager
-
PlateSpin User
-
PlateSpin Datastore Manager
-
PlateSpin Network Manager
-
PlateSpin Cluster Manager
-
PlateSpin VM User
-
-
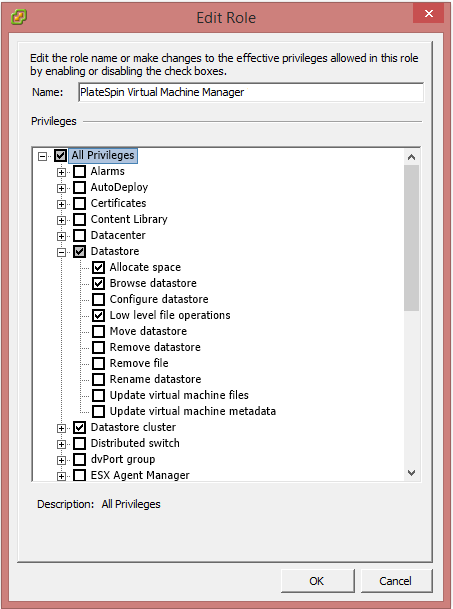
Click Edit to view the privileges settings in the Edit Role dialog.
For example, the following figure shows some of the privileges set for the PlateSpin Virtual Machine Manager role.