32.2 Automated Migration to VMware Using Migrate Client
-
Discover or refresh your source workload and your target VM host.
-
In the Migrate Client, initiate a peer-to-peer workload migration.
-
Expand the Tasks options, then select the conversion type, depending on your goals for the migration:
-
Copy Workload
-
Move Workload
The Source and Target panes display workloads and targets applicable to the selected type of a migration job.

-
-
In the Source pane, select the workload you want to migrate.
-
In the Target pane, select target host for the migration.
-
Check the validation messages at the bottom of the window.
-
Click Configure Job to access the Peer-to-Peer Migration Job window.
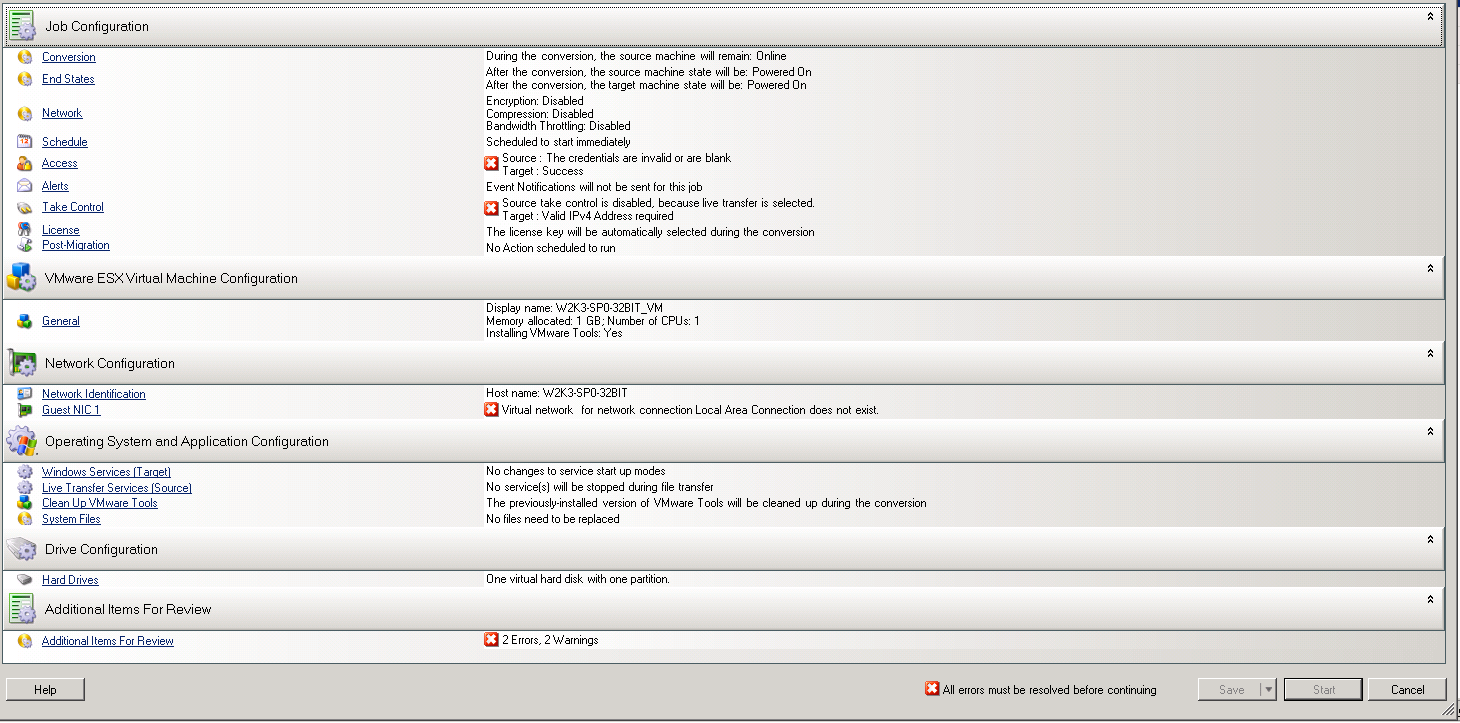
Figure 32-1 Peer-to-Peer Migration Job Window
-
-
In the Job Configuration section of the Migration Job window, configure the following settings:
Setting Name
Description
License
PlateSpin Migrate automatically selects the best license key for a migration job. If you have multiple license keys, you can specify the license key to use for the workload, assuming licenses are available (neither expired nor exhausted).
To specify an alternate key to use:
-
Deselect Automatically select the best license key during the conversion, then select the appropriate license key from the menu.
-
Click OK.
The selected license key is displayed on the License tab and its description is updated.
Conversion
Transfer Scope
Specify the scope of workload data to transfer from the source to the target as Full Migration or Server Sync (Changes Only).
Transfer Method
Specify how data is transferred from source to target. The availability depends on your workload and migration job type.See Supported Data Transfer Methods.
Source Machine End State
Specify whether to shut down the source workload after a successful cutover. For a workload move, the shut down is selected by default.
Target Virtual Machine End State
Specify whether to power on, power off, or suspend the target workload after a successful cutover.
Network
Compression
Specify whether to compress data during transmission between the source and target workloads, and the level of data compression to apply.See Data Compression. Select one of the following options:
-
Fast: Consumes the least CPU resources on the source, but yields a lower compression ratio.
-
Optimal: Consumes optimal CPU resources on the source and yields an optimal compression ratio. This is the recommended option.
-
Maximum: Consumes the most CPU resources on the source, but yields a higher compression ratio.
Encryption
Select Encrypt Data Transfer to encrypt the data as it is transferred from source to target.See Security and Privacy.
Bandwidth Throttling
Specify whether to throttle bandwidth for data transfer traffic between the source and target machines. To enable throttling, select the Enable Bandwidth Throttling option, specify the required maximum value in Mbps, and optionally a time period during which to enforce the throttling. If specified, the from and to time values are based on the source workload’s system time.
If no time interval is defined, bandwidth is throttled to the specified rate at all times by default. If time interval is defined and the migration job executes outside this interval, data is transferred at full speed.
IP Addresses
Specify additional IP addresses for source workloads to enable communication in environments that use network address translation (NAT).
For information on how to specify additional IP addresses for your PlateSpin Server, see Migrations Across Public and Private Networks through NAT.
Schedule
Schedule
Specify when to start the migration job:
-
Run immediately
-
Run at a later time
Use the calendar menu to specify the date and time to begin the migration.
NOTE:You must prepare the workload prior to the scheduled time.The full replication cannot run unless the target VM exists and the workload preparation is complete. Migrate skips the scheduled full replication and retries it at the next scheduled time.
Source Credentials
(Windows) Specify the account user name with local or domain-level administrative privileges and a valid password. Use this format:
-
For domain member machines: authority\principal
-
For workgroup member machines: hostname\principal
(Linux) Specify the root or root-level user name and a valid password.
Target Credentials
(VMware DRS Cluster) Specify VMware vCenter Web service user name and password.
(VMware ESX Server) Specify one of the following:
-
ESX account with administrator role
OR
-
Windows domain credentials (versions 4 and 4.1 only)
Alerts
Receive Event Notifications
Specify whether to send email notifications for event conditions. You must configure an SMTP server to use this feature.
Receive Progress Notifications
If you enable Event notifications, you can optionally receive progress notifications at a specified interval.
Send to Addresses
Add or remove valid email addresses for recipients of the notifications.
Take Control Settings
Target Virtual Machine
Under Target Virtual Machine, click Configure, then specify the options for the virtual network and the TCP/IP settings for the replication NIC, then click OK.
Post-Migration
Action
Specify a pre-configured action from the PlateSpin Migrate library.See Managing Post-Migration Actions (Windows and Linux).
Execution Parameters
Specify the command line command to run the selected action. You can specify a timeout for the execution.
Credentials
Specify the user name and password to use for the post-migration tasks. You can optionally use the source credentials.
-
-
In the Virtual Machine Configuration section of the Migration Job window, click General, then configure the following settings:
Setting Name
Description
VMware ESX Virtual Machine
Virtual Machine Name
Specify a name to use for the target VM as it appears in the VMware.
Datastore
Select a datastore associated with your VM for storing VM configuration files.
Path
Type the path to use for the target VM file, including the VM file name. For example:
/hostname-VM/hostname-VM.vmx
Virtual Machine Memory Allocation
Specify the amount of virtual memory in GB.
Install VMware Tools
Specify whether to install the latest VMware tools on the target VM. If they are installed on the source, they will be uninstalled and reinstalled using the version appropriate for the platform of the VMware target host.
Virtual Devices
Specify preferences for the virtual devices.
Advanced
(For expert users) Specify preferences for the Resource Pool, number of CPUs, and CPU scheduling affinity based on their availability on the target VMware server. Each vCPU is presented to the guest OS on the VM platform as a single core, single socket.
(For migration to VM platform that is part of a DRS Cluster) Specify the Resource Pool location where the migrated VM is to be created.
PlateSpin Migrate displays target virtual machine configuration options specific to the selected target and also provides access to advanced configuration options. For information about host-specific configuration options, see:
-
In the Network Configuration section of the Migration Job window, configure the following settings:
Setting Name
Description
Network Configuration
Network Identification Settings for Windows
Host Name
Specify the desired host name for the target machine.
Generate New SID
When this option is selected, the target workload is assigned a new System Identifier (SID). Credentials are required only for Windows 2008 systems, and must be the credentials for the local (embedded) Administrator account. If this account has been locally renamed on the source, provide the new name.
Member of Domain / Workgroup
Select the required option and type the name of the domain or workgroup that you want the target machine to join.
Preserve Source Server’s Domain Registration
Preserves domain registration and ensures that the source server domain registration remains intact during migration. If you disable this option, the source machine’s domain account is transferred to the target machine. The source server still appears to be on the domain, but does not have a valid connection.
Domain Credentials
If the target machine is to be part of a domain, specify valid credentials for a user account with permission to add servers to the domain, such as a member of the Domain Admins group or Enterprise Admins group.
Network Identification Settings for Linux
Host Name
On the Network Identification tab, specify the desired host name for the target machine.
DNS
Use the Add, Edit, and Remove buttons to manage DNS server entries for the new virtual machine.
-
In the Operating System and Applications Configuration section of the Migration Job window, configure the following settings:
Setting Name
Description
Operating System and Application Configuration
Windows Services (Target)
Select Windows services’ start conditions on the target VM after cutover. Start options are Automatic, Manual, Disabled, and Automatic (Delayed Start).
To modify the settings:
-
Click the Status column for the service, then select from the Windows start options.
-
When you are done setting services start states, click OK.
Live Transfer Services (Source)
Specify the Windows services to stop on the source workload during live data transfers.
We recommend that all the non-VSS compliant services or antivirus are stopped temporarily on the source while the VSS snapshot is being captured on the source. Select the Windows services that you want to be temporarily stopped on the source workload while the VSS snapshot is being captured on the source. These services are restored as soon as the VSS snapshot creation completes.
To modify the settings:
-
Select Stopped next to the service to be stopped for live data transfer.
-
When you are done setting services to stop, click OK.
Linux Daemons (Target)
Specify the start states for daemons on the target VM after cutover.
To modify the settings:
-
Click the Run Level column for the daemon, then select from run levels 0 through 6 and Boot (B), then click OK.
-
When you are done setting daemon start states, click OK.
Live Transfer Daemons (Source)
Specify the daemons to stop on the source workload during live data transfers.
To modify the settings:
-
Select Stopped next to the daemon to be stopped for live data transfer.
-
When you are done setting daemons to stop, click OK.
-
-
In the Drive Configuration section of the Migration Job window, configure the following settings:
Setting Name
Description
Drive Configuration
Hard Drives
Specify drive and volume configurations to be migrated.
Disks
Specify the path to the hard disk on the target virtual machine.
Volumes
Select volumes to be included in the target for migration.
NTFS Cluster Size
(For File-Based Windows Workloads) Specify the cluster size for the NTFS volume. For information about the default cluster size for an NTFS volume, see the Microsoft Support KB Article 140365.
Non-volume Storage
(For Linux Workloads) Specify a non-volume storage, such as a swap partition, that is associated with the source workload. This storage is re-created in the migrated workload.
Disks For Volume Groups
(For Linux Workloads) Specify the datastore name and the path where the virtual disk must be created on the target machine. You can choose to retain the path specified by default.
Volume Groups
(For Linux Workloads) Specify the LVM volume groups to be migrated with the LVM logical volumes listed in the Converted Logical Volumes section of the settings.
Converted Logical Volumes
(For Linux Workloads) Specify one or more LVM logical volumes to be migrated for a Linux workload.
PlateSpin Migrate displays storage configuration options specific to the selected target. For information about host-specific configuration options, see:
-
In the Additional Items for Review section of the Migration Job window, review errors and messages about the workload configuration. You must resolve errors before you can submit the migration job.
-
Click OK.
32.2.1 Target VM Configuration: VMware ESXi 5 and Later
The following are configuration options specific to VMware vSphere 5 and later (applicable to all VMs under the containing resource pool).

|
|
Name: Specify the display name for the new virtual machine. CPU Resources
Memory Resources: (these are similar to CPU resource settings, but apply to memory resources) |
32.2.2 Target VM Configuration: VMware ESX 4.1
The following are configuration options specific to VMware ESX systems prior to vSphere 5. To access settings that control resource pools, the number of CPUs, and CPU scheduling affinity, click Advanced.

Virtual Machine Name: Specify the display name for the new virtual machine. Datastore: Select the datastore where you want to create the *.vmx file. Configuration File Path: Specify a name and the directory path for the virtual machine’s *.vmx configuration file. Virtual Machine Memory Allocation: Specify a value for the amount of virtual RAM to be assigned to the virtual machine. Install VMware Tools: Enable this option to install VMware tools during the migration process (recommended). SCSI Drives: Select either BusLogic or LSIlogic (the recommended option). Advanced: Click this button to view or modify advanced VM configuration settings. |

Resource Pool: If required, assign your target VM to a resource pool. When no resource pool is specified, the VM is assigned to the root resource pool. Number of CPUs: Select the required number of CPUs to assign to the target VM. For example, you can convert a single-processor workload to a multi-processor VM, or a multi-processor workload to a single-processor VM. CPU Scheduling Affinity: Represents which ESX Server processors the virtual machine can run on (if your ESX Server is a multiprocessor system). Specify the required processor or select Default (recommended). For details, see your VMware documentation. |
32.2.3 Drive Configuration: VMware ESX
The following are drive configuration settings specific to VMware ESX:

|
|
|
Datastore: Select the datastore volume on the ESX server where you want to place the vmdk files. Copy: Select the volumes to be copied during the migration. New Free Space: To resize the volume during the migration, specify the desired amount of free space. PlateSpin Migrate automatically adjusts New Size. New Size: To resize the volume during the migration, specify the desired size. PlateSpin Migrate automatically adjusts New Free Space. Disk/Volume Group: Assign the volume to a disk or, if LVM is enabled, to a volume group. The volume will be copied to this disk or volume group on the target machine. Create: Select any non-volume disk partitions that should be created on the target machine (for example, a Linux swap partition). New Size: To resize the non-volume partition during the migration, specify the desired size. |