26.2 Managing Files and Folders on NSS Volumes Using iManager
26.2.1 Creating a Folder on an NSS Volume
As an administrator, you can use the Files and Folders plug-in to iManager to create a folder on an NSS volume.
Prerequisites
-
The destination NSS volume must be in the same tree where you are currently logged in to iManager.
-
You must have trustee rights for the volume and destination location where you want to create the new folder. The Create right is required for creating files and folders.
Procedure
-
In iManager, click Files and Folders, then click New Folder to open the New Folder page.

-
Use one of the following methods to specify the destination path on the NSS volume where you want to create the new folder:
-
Click the Search icon to browse and locate the destination folder, then click the name link of the folder to select it.
-
Click the History icon to select a folder from the list of folders that you recently accessed.
The pathname of the folder appears in the Path field.
-
-
In Folder Name, type the name the folder you want to create in the selected location.
-
Click OK to create the folder, or click Cancel to abandon it.
A message confirms when the folder has been successfully created.
-
Click Repeat Task to create another folder, or click OK to dismiss the confirmation message.
-
Click Files and Folders, then click Properties to set file system trustees, trustee rights, and attributes for the new folder or folders.
For instructions for configuring properties, see Section 21.1, Configuring File System Trustees, Trustee Rights, Inherited Rights Filters, and Attributes.
26.2.2 Deleting a File or Folder on an NSS Volume
As an administrator, you can use the Files and Folders plug-in to iManager to delete a file or folder on an NSS volume.
Prerequisites
-
The NSS volume must be in the same tree where you are currently logged in to iManager.
-
You must have trustee rights for the file or folder that you want to delete. The Erase right is required to delete the file.
Procedure
-
In iManager, click Files and Folders, then click Delete to open the Delete File or Folder page.

-
Use one of the following methods to specify the file or folder that you want to delete from the NSS volume:
-
Click the Search icon to browse and locate the file or folder, then click the name link of the object to select it.
-
Click the History icon to select a file or folder from the list of files and folders that you recently accessed.
The pathname of the folder appears in the Name field.
-
-
Click OK to delete the selected file or folder, or click Cancel to abandon the delete process.
A message confirms when the file or folder has been successfully deleted.
-
Click Repeat Task to delete another folder, or click OK to dismiss the confirmation message.
26.2.3 Uploading Files to an NSS Volume
As an administrator, you can use the Files and Folders plug-in to iManager to upload files from your local computer to an existing folder on an NSS volume.
Prerequisites
-
The destination NSS volume must be in the same tree where you are currently logged in to iManager.
-
You must have trustee rights for the destination folder in order to be able to find the folder and upload the file. The Create right is required for file uploads.
Procedure
-
In iManager, click Files and Folders, then click Upload to open the Upload File page.

-
Use one of the following methods to specify the path to the folder on the NSS volume where you want to put the file:
-
Click the Search icon to browse and locate the folder, then click the name link of the folder to select it.
-
Click the History icon to select a folder from the list of folders that you recently accessed.
The pathname appears in the Path field.
-
-
Select the file on your local computer that you want to upload:
-
Click Browse to open a local file browser dialog box.
-
Browse and locate the file.
-
Select the file, then click Open.
The local pathname for the selected file appears in the File Name field.
-
-
Click OK to begin the upload, or click Cancel to abandon the process.
A message confirms when the file has been successfully uploaded. Wait until the upload completes before proceeding to other tasks.
-
Click Repeat Task to upload another file, or click OK to dismiss the confirmation message.
26.2.4 Downloading Files from an NSS Volume
As an administrator, you can use the Files and Folders plug-in to iManager to download a file from an NSS volume to your local computer.
Prerequisites
-
The NSS volume must be in the same tree where you are currently logged in to iManager.
-
You must have trustee rights for the file in order to be able to browse to and download the file.
Procedure
-
In iManager, click Files and Folders, then click Download to open the Download File page.

-
Use one of the following methods to select the file that you want to download from the NSS volume to your local drive:
-
Click the Search icon to browse and locate the file, then click the name link of the file to select it.
-
Click the History icon to select a file from the list of files that you recently accessed.
The pathname appears in the File Name field.
-
-
Click OK to open the File Download dialog box.
IMPORTANT:If the File Download dialog box does not open, make sure the security settings in your browser allow downloads from the server by adding the server as a trusted site, then try again.
-
Use one of the following methods to save the file to the local computer:
-
Click Open to view the file in an appropriate application, then save the file by using the application's File > Save options.
The application that opens the file must already be installed on your computer.
-
Click Save to open the Save As dialog box, browse to an existing folder or create a new local folder where you want to save the file, then click Save.
The browser’s download manager manages the download and notifies you when the download is complete.
You can continue with other iManager tasks while the file is downloading.
-
26.2.5 Renaming a File on an NSS Volume
Use this task to rename your file to a different name.
Prerequisites
You must have trustee rights for the file in order to be able to find the file and rename it the file. Create and modify rights are required to rename the files.
Procedure
-
Use one of the following methods to select the file that you want to rename:
-
Click the Search icon to browse and locate the file, then click the name link of the file to select it.
-
Click the History icon to select a file from the list of files that you recently accessed.
The pathname appears in the Path field.
-
-
Type the new name in the New name field.
-
Click OK to rename the file, or click Cancel to discard the changes.
A message confirms that the file has been successfully renamed. Wait until the rename completes before proceeding to other tasks.
26.2.6 Moving a File to Different Folder on an NSS Volume
Use this task to move your file to a different folder on the same NSS volume.
Prerequisites
You must have trustee rights for the file in order to be able to find the file and move it. Create and modify rights are required to move a file.
Procedure
-
Use one of the following methods to select the file that you want to move:
-
Click the Search icon to browse and locate the file, then click the name link of the file to select it.
-
Click the History icon to select a file from the list of folders that you recently accessed.
-
-
Click Browse to open a local file browser dialog box. Browse to locate and select the folder where you want to move the file, then click Open.
The pathname for the selected folder appears in the Folder Name field.
-
Click OK to begin the upload, or click Cancel to discard the changes.
A message confirms that the file has been successfully uploaded. Wait until the upload completes before proceeding to other tasks.
26.2.7 Viewing or Modifying File or Folder Properties
-
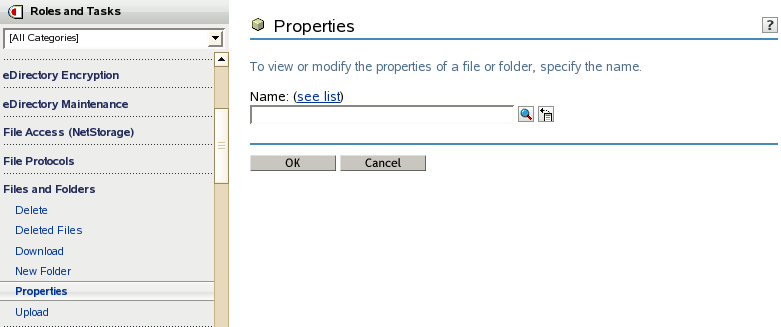
In iManager, click Files and Folders > Properties to open the Properties page.
-
Click the Search icon to browse the Storage objects, locate and select the name link of the file or folder you want to manage, then click OK to view the Properties for the file.
-
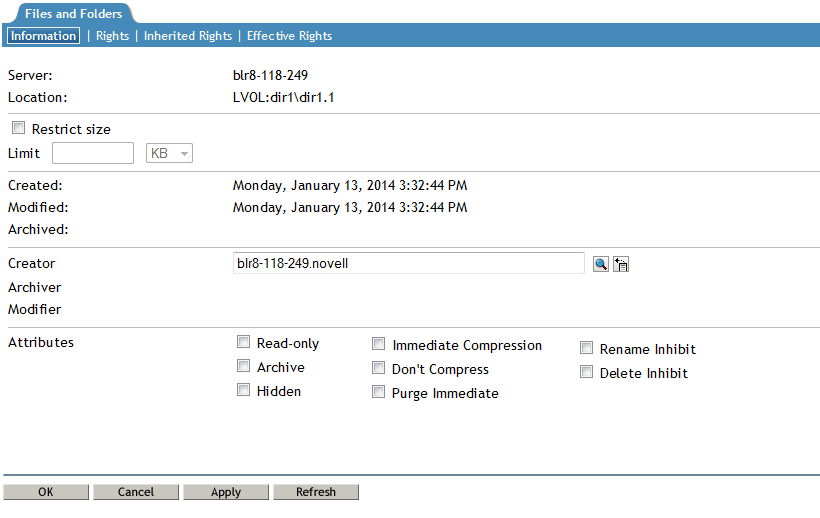
Click the Information tab to view or modify the following information for the selected folder or file:
Property
Description
Server
The name of the server.
Location
The pathname of the selected volume, folder, or file. For example:
VOL1:dir1\dirB\filename.ext
Size
The file size.
Restrict Size
(Enable or Disable a Directory Quota on a Folder)
Enable (select) or disable (deselect) a directory quota on the specified folder on an NSS volume where the Directory Quotas attribute is enabled. The default is Disabled.
If this option is enabled, you must also specify a value for the quota in the Limit field.
A directory quota limits the amount of space on a volume that can be consumed by all of the files and folders in that directory. The directory quota applies to files and folders created by any user of the directory.
Select Restrict Size to enable a directory quota for the selected folder, specify the quota value in Limit, then click Apply.
Deselect Restrict Size to disable a directory quota for the selected folder, then click Apply.
Limit
(Set Limit for a Directory Quota on a Folder)
The maximum size allowed for the specified directory and its contents.
Default: Disabled (not available unless Restrict Size is enabled).
If you enable Restrict Size for the selected folder, you must specify a limit for the directory quota. Type a value in KB for the quota. The value must be an increment of 4 KB; that is, it must be divisible by 4 with no remainder. Click Apply to save the changes.
If the directory quota exceeds the volume quota, the volume quota is enforced.
If the current size of the selected folder exceeds the specified limit, users cannot save data to the folder until space is cleared by removing files from it.
If a user quota is set for a user on the volume, the user space restriction overrides the directory quota. That is, the user cannot save data to the folder if doing so causes the user to exceed his or her user quota.
Created
The time stamp (Day, Month DD, YYYY hh:mm) for when the file or folder was created.
Modified
The time stamp (Day, Month DD, YYYY hh:mm) for when the file or folder was last modified.
Accessed
The time stamp (Day, Month DD, YYYY hh:mm) for when the file or folder was last accessed.
Archived
The time stamp (Day, Month DD, YYYY hh:mm) for when the file or folder was last archived.
Creator
(View or Modify Ownership)
The typeless distinguished NetIQ eDirectory username (such as username.context) of the user who created the file or folder. If the username becomes invalid, such as if an employee leaves the company, the GUID of the username is reported. For NSS, any number of files or folders can be represented by GUIDs instead of valid usernames.
User quotas for NSS volumes consider file ownership to enforce user space restrictions. You might need to change the ownership of a file or folder in order to make the space it consumes be charged against a different user.
For NSS volumes (as for all volumes that use the OES trustee model of access), all access to data is controlled by file system trustees and trustee rights instead of by ownership. When a user creates a file or folder, the trustees and trustee rights for accessing the file are automatically inherited from the directory where the file is created. If you intend different trustees and rights for the file, you must assign them explicitly by user, or assign the rights to a group and put the users into that group. For instructions, see Configuring Rights Properties (File System Trustees, Trustee Rights, and Inherited Rights Filter).
Changing the ownership of the file or folder does not modify who can access it, but it does modify whose username is charged for the space it consumes. If you modify the ownership, you must click Apply or OK to save the changes.
Archiver
The distinguished username (such as username.context) of the user who modified the version of the file or folder that was last archived.
Modifier
The distinguished username (such as username.context) of the user who last modified the current version of the file or folder.
Attributes
File attributes determine how the file or folder behaves when accessed by any user. Enable or disable an attribute by selecting or deselecting the check box next to it. If you modify a setting, click Apply or OK to save the changes.
File attributes apply universally to all users. For example, a file that has a read-only attribute is read-only for all users.
Attributes can be set by any trustee with the Modify right to the directory or file, and attributes stay set until they are changed. Attributes do not change when you log out or when you down a file server.
For example, if a trustee with the Modify right enables the Delete Inhibit attribute for a file, no one, including the owner of the file or the network administrator, can delete the file. However, any trustee with the Modify right can disable the Delete Inhibit attribute to allow the file’s deletion.
The following table defines file system attributes and whether they apply to files, folders, or both files and folders.
Attribute
Description
Files
Folders
Read Only
Prevents a file from being modified.
This attribute is typically used in combination with Delete Inhibit and Rename Inhibit.
Yes
No
Archive
Identifies files and folders that have been modified since the last backup. This attribute is assigned automatically.
Yes
Yes
Hidden
Hides directories and files so they do not appear in a file manager or directory listing.
Yes
Yes
Shareable
Allows more than one user to access the file at the same time. This attribute is usually used with Read Only.
Yes
No
Purge Immediate
Flags a directory or file to be erased from the system as soon as it is deleted. Purged directories and files cannot be recovered.
Yes
Yes
Rename Inhibit
Prevents the directory or filename from being modified.
Yes
Yes
Delete Inhibit
Prevents users from deleting a directory or file.
This attribute overrides the file system trustee Erase right. When Delete Inhibit is enabled, no one, including the owner and network administrator, can delete the directory or file. A trustee with the Modify right must disable this attribute to allow the directory or file to be deleted.
NOTE:Setting the following preferences override the delete inhibit and rename inhibit settings. The override option is made available via volume mount options and nsscon.
-
From nsscon enter, /(No)RootOverrideFA=(ALL|VOL1,VOL2)
-
For local volumes change the following: /etc/fstab (-o name=<NAME>,overrideFA)
-
For shared volumes change the following: cluster resource load scripts (/opt=overrideFA)
If /RootOverrideFA is set on the volume, the Linux root user can delete and rename a file.
Yes
Yes
-
-
If you modified any settings, click Apply or OK to save your changes.
26.2.8 Viewing or Modifying File Ownership
The owner of a file is assigned by default to be the identity of the user who creates the file. Ownership does not determine who can access a file because the NSS file system uses the OES trustee model to control access. However, user quotas for NSS volumes consider file ownership to enforce user space restrictions. You might need to change the ownership of a file or folder in order to make the space it consumes be charged against a different user. Changing the ownership of the file or folder does not modify who can access it, but it does modify whose username is charged for the space it consumes.
NOTE:As an administrator you can modify the file or folder ownership.
The Creator field shows the typeless distinguished NetIQ eDirectory username (such as username.context) of the user who owns the file or folder. If the username becomes invalid, such as if an employee leaves the company, the GUID of the username is reported. For NSS, any number of files or folders can be represented by GUIDs instead of valid usernames.
-
In iManager, click Files and Folders, then click Properties to open the Properties page.
-
Click the Search icon to browse and locate file from the Storage objects, click the name link of the file to select it.
The pathname of the file or folder appears in the Name field.
-
Click OK to open the file’s Properties page.

NOTE:For an AD user, the creator field will be empty.
-
On the Information page, the Creator field shows the typeless distinguished username of the current owner, such as username.context.

-
If you want to modify the owner, click the Search icon to open the Object Browser dialog box, then locate and select the username of the new owner. iManager cannot be used to change the owner to an AD user. Use the nsschown command line tool (Section B.14, nsschown).
-
If you modified the owner, click Apply or OK on the Information page in order to save the change.
26.2.9 Viewing, Adding, Modifying, or Removing a Directory Quota
Directory quotas for NSS volumes require that the Directory Quotas attribute be set for the volume. For information, see Section 23.5.1, Enabling or Disabling the Directory Quotas Attribute for an NSS Volume.
-
In iManager, select Files and Folders > Properties.
-
Click the Search icon, browse to locate and select the folder you want to manage on an NSS volume, then click OK to open the Properties page for the selected folder.
-
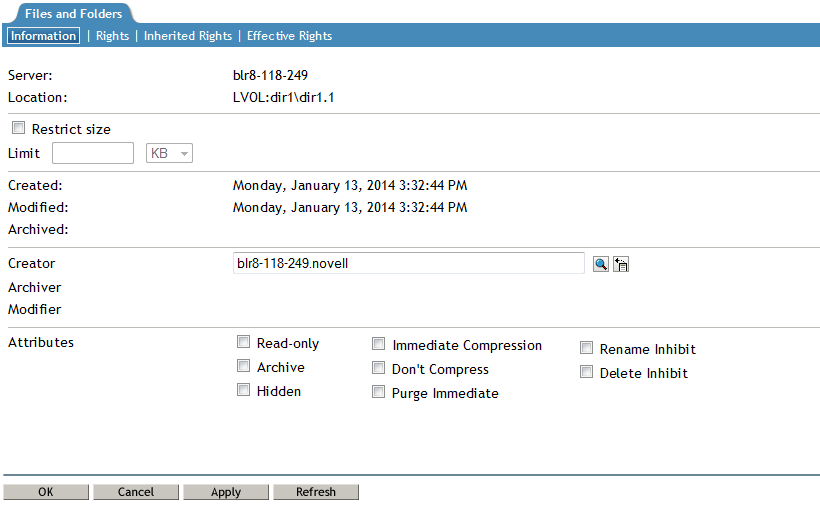
View the current status of the Directory Quota.
If a Directory Quota is set, the Restrict Size field is selected and the Limit field shows the quota size in KB.

If the Directory Quota is not set, the Restrict Size field is deselected and the Limit field is dimmed (grayed out).

-
Do one of the following:
-
Add a Quota: On the Information tab, select Restrict Size to enable space restrictions for the selected directory. In the Limit field, type the directory quota in KB. The value must be an increment of 4 KB; that is, it must be divisible by 4 with no remainder.
-
Modify an Existing Quota: In the Limit field, type the new directory quota in KB. The value must be an increment of 4 KB; that is, it must be divisible by 4 with no remainder.
-
Remove a Quota: On the Information tab, deselect Restrict Size to disable space restrictions for the selected directory. The Limit field is automatically dimmed (grayed out).
-
-
On the Information page, click Apply or OK to apply the changes.