1.2 Understanding Virtualization
Virtualization can be used at multiple computing levels to provide services for your enterprise.
1.2.1 Where Is Virtualization Today?
Virtualization of servers and services is everywhere:
-
Virtualization with hardware, such as blade centers or Cisco Unified Computing System (UCS).
-
Virtualization with software, such as VMware, XEN, KVM, Hyper-V, and more.
-
Virtualization within the infrastructure:
-
Network: VLAN
-
SAN: port virtualization in the SAN
-
Storage virtualization
-
1.2.2 Why Use Virtualization?
The benefits of virtualization include the following:
-
Allows consolidation of servers to help reduce costs for hardware and power.
-
Allows independence of servers from hardware and environmental complexities and infrastructure.
-
Allows scalability of services on a single server because the hardware is more powerful than one service needs.
-
Increases server and service availability.
-
Allows you to use cloud services.
-
Builds independence from hardware to gain the flexibility of managing hardware connectivity on only the virtualization level.
1.2.3 Why Use OES Cluster Services?
The benefits are:
-
Increases service availability, minimizing recovery time when problems occur
-
Consolidation
-
Flexibility
-
Scalability
-
Manageability
-
Hardware independence
1.2.4 Server versus Service Virtualization
Virtualization can occur on different levels in the computing environment. The difference between a server and a service is summarized in Table 1-1. A server consists of hardware, an operating system environment made up of the kernel and hardware drivers, one or more services, and a process scheduler to control the services. A service consists of data and the service configuration settings, the application that provides the service (including its process, code, and executable), and a network address to give users access to the service.
Table 1-1 Server versus Service
|
Server with Operating System |
Service |
|---|---|
|
|
In a virtualized environment, a server can be virtualized as a virtual machine that is independent of the hardware. Virtualization hypervisors such as Xen, KVM, VMware, and Hyper-V allow virtualization of servers.
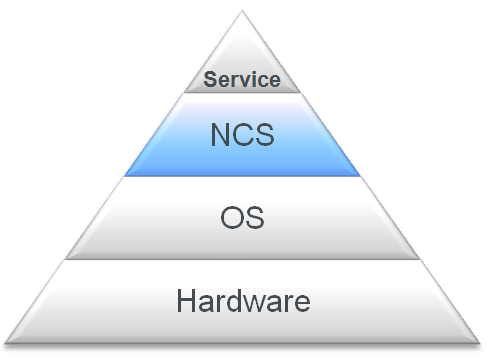
Figure 1-2 Virtualization Stack
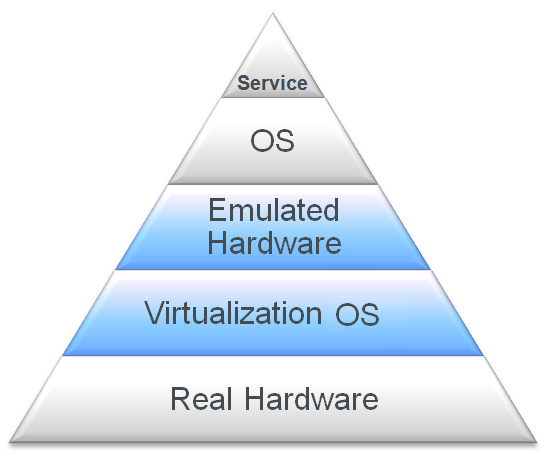
With NCS, a service can be virtualized as a cluster resource that can be failed over between nodes. Clustering makes the service independent of the hardware.
Figure 1-3 Server Stack