10.5 SLP
The OpenSLP services on OES are compatible and comparable with NetWare SLP services.
This section discusses the following topics:
10.5.1 Overview
The Service Location Protocol (SLP) was developed so that clients and other software modules can dynamically discover and use services on the network without knowing the IP address or the hostname of the server offering the service.
Why SLP Is Needed
NetWare: Although many other applications and server types rely on SLP for service discovery, NetWare services are actually integrated with eDirectory, and if eDirectory is configured correctly, the services work without SLP. However, SLP is automatically provided on NetWare for other services that might be installed.
OES: On the other hand, for OES services to work, the server must either:
-
Have an eDirectory replica installed.
This is not automatic after the third server installed in a tree, nor is having more than three to five replicas on servers in the tree recommended.
-
Have eDirectory registered with the OpenSLP service running on the server.
This requires SLP configuration either during the OES installation or manually.
About the Three SLP Agents and Their Roles
Three software “agents” provide the infrastructure for SLP-based service discovery:
-
Service Agents (SAs): Are a required component of any SLP infrastructure. They act on behalf of a network service that is running on a server by advertising that the service is available.
-
User Agents (UAs): Are also required. They act on behalf of clients or other software modules that need network services by searching for the needed services.
-
Directory Agents (DAs): Are technically optional, but they are used in most SLP infrastructures. They collect service information from Service Agents so that User Agents can more easily locate the services. DAs are like a phone book directory listing of services on the network.
DAs are not needed when all of the SAs and UAs are on the same subnet. This is because the UAs and SAs can find each other within the subnet using multicast packets, provided that there are no firewalls that are set to block multicast traffic.
Overcoming the Subnet Limitation
OpenText recommends against routing multicast packets across subnet boundaries, and most network configurations conform with that recommendation. Therefore, when SAs and UAs are on different subnets, they need an alternative to multicasting for advertizing and locating services on the other subnets.
Network administrators use DAs to solve this problem by setting up organizational or geographical DAs and then configuring the SAs and UAs within the organization or geographical area to use them. Many administrators further subdivide the DA workload by defining multiple SLP scopes based on different kinds of network services, and then configuring the SAs and UAs to communicate with the DAs servicing the scope that pertains to them.
An eDirectory Example
When you configure eDirectory during an OES server installation, you have the option of specifying one or more SLP DAs for the server to communicate with. Each time eDirectory starts and every hour thereafter, the server’s SA will send a unicast packet to the server’s assigned DAs, advertising that its eDirectory services are available.
IMPORTANT:Prior to eDirectory 8.8.2, the eDirectory SA advertised service availability every 10 minutes by default. Starting with eDirectory 8.8.2, the refresh interval changed to one hour. This has caused some confusion for network administrators who couldn’t figure out why it took so long for eDirectory to register as a service
For information on how to set the refresh interval to a smaller value, see TID 7001449 in the OpenText Support Knowledge base.
What Happens When a DA Goes Down?
As you can imagine, a directory agent in a large organization can accumulate many service listings after it has been running for a while. Unfortunately, because DAs are inherently cache-only repositories, if they go down for some reason, when they come back up their list of services is initially blank.
Novell SLP solved this problem on NetWare 5.x and later through eDirectory Modified Event notifications. These notifications keep all of the NetWare DA's that are servicing the same scope in sync with each other. After going down and coming back up, a NetWare DA can quickly recover its directory listings.
OpenSLP DA's, on the other hand, have historically been completely independent from each other. Because they are not eDirectory-aware, they have had no means of recovering the directory listings they had prior to going down.
This changed, beginning in OES 2 SP3.
OpenSLP DAs can now
-
Retrieve and/or push service information to and/or from other DAs. For more information, see Synchronizing Data Between OpenSLP DAs and/or Novell SLP DAs.
-
Back up their service registrations so that when the DA service is started up it can read the backup file and pre-populate its cache. For more information, see Backing Up Registrations and Managing Persistence.
These changes provide, in effect, the same type of DA to DA communication for OES that has traditionally been available only on NetWare.
10.5.2 Comparing Novell SLP and OpenSLP
Table 10-4 SLP Solutions
|
Platform |
NetWare |
OES |
|---|---|---|
|
SLP Solution |
Novell SLP |
OpenSLP |
|
About the Solution |
The Novell version of SLP adapted portions of the SLP standard to provide a more robust service advertising environment. Novell SLP remains the default discovery mechanism for NetWare 6.5 SP8 servers. However, all NetWare service components that engage in discovery, including Client for Open Enterprise Server software, can use alternative mechanisms such as DNS, eDirectory, or local host configuration files. |
OpenSLP is an implementation of various IETF specifications, including RFC 2614 (SLP version 2.0). It is the default SLP service installed on SLES 15. In OES, OpenSLP is available for those applications that require it. The default discovery mechanism is actually DNS, but SLP must be present for any applications that require it, especially in those cases where the OES server is the fourth or later server added to a tree and doesn’t have an eDirectory replica automatically installed. |
|
Differences |
Novell SLP directory agents (DAs) store service registrations for their SLP scope in eDirectory. As a new service registration is stored in eDirectory, other DAs assigned to the same scope are notified so that they can refresh their caches with the latest service information. Also, when a Novell SLP DA starts up, it immediately populates its cache with the latest service information stored in eDirectory. NOTE:Novell SLP DAs do not directly share information with each other as many administrators have assumed. But they do maintain well synchronized caches through eDirectory as described above. |
OpenSLP directory agents (DAs) are able to share service registrations as described in Synchronizing Data Between OpenSLP DAs and/or Novell SLP DAs. OpenSLP is also capable of ensuring data persistence when DAs go down, as explained in Backing Up Registrations and Managing Persistence. |
|
Compatibility |
Novell SLP user agents (UAs) or service agents (SAs) can access both Novell SLP DAs and OpenSLP DAs. |
OpenSLP-based user agents or service agents can access both Novell SLP DAs and OpenSLP DAs. |
|
Documentation |
|
10.5.3 Setting Up OpenSLP on OES Networks
SLP services are always installed as part of both NetWare and OES. On NetWare and on OES, SLP services run automatically in multicast mode. Setting up directory agents and multiple scopes, etc. requires a manual configuration of SLP, either during the installation or by modifying the slpd.conf file afterward.
When Is OpenSLP Required?
The OES install automatically starts OpenSLP on your OES server in case any of the following applies:
-
You install more than three servers into a new tree
-
You create a new eDirectory partition on an OES server.
-
You either don’t have an existing Novell SLP service, or you don’t want to continue using Novell SLP.
IMPORTANT:If you need to set up OpenSLP in more than multicast mode for the reasons above, it is most convenient if you do it before you install the fourth server in your tree or partition. That way you can point to the SLP service during the installation. Setting up SLP services on every OES server is recommended.
Setting Up an OpenSLP DA Server
The default SLP configuration in the YaST-based install doesn’t include having a Directory Agent. This approach is far less robust, requires multicasting, and involves disabling the firewall.
If you need OpenSLP and you don’t already have an OpenSLP Directory Agent (DA) set up on your network, for simplicity’s sake we recommend that you set up the first OES server in your tree as an OpenSLP DA. The simplest way to do this is during server installation by selecting the Configure as Directory Agent option in the YaST-based installation.
After creating the DA, you can then configure all subsequently installed servers to either point to that DA or to other DAs you create later.
To set up an OpenSLP DA on an existing OES server, do the following.
-
On the OES server that will become the DA, open the /etc/slp.conf file in a text editor.
-
In slp.conf, remove the semicolon [;]) from the beginning of the following line:
;net.slp.isDA = true
so that it reads
net.slp.isDA = true
-
Find the following line:
;net.slp.useScopes = myScope1, myScope2, myScope3
IMPORTANT:The example in the configuration file is misleading because the spaces after each comma are not ignored as one might expect them to be.
Therefore, the scope names created or configured by the statement after the first comma actually have leading spaces in them. For example, the first scope name is
myScope1
but the scope names that follow it all have leading spaces,myScope2
,myScope3
and so on. This is a problem, especially if one of the later names becomes the first name in a subsequent SLP configuration and the leading space is ignored.If you use the scopes given in the example, remove the spaces between the entries.
-
Modify the line by removing the semicolon and typing the name of the scope you want this DA to use to provide service information on the network. For example, you might change the line as follows:
net.slp.useScopes = Directory
IMPORTANT:Although SLP provides a default scope if no scope is specified, it is always good practice to define one or more scopes by configuring the net.slp.useScopes parameter in slp.conf.
Scopes group and organize the services on your network into logical categories. For example, the services that the Accounting group needs might be grouped into an Accounting scope.
More information about scope planning is available on the OpenSLP Web site.
When no scope is specified, all services are registered in a scope named Default.
-
Configure the firewall on the DA server to allow SLP daemon traffic:
-
In the YaST Control Center, click Security and Users > Firewall.
-
In the left navigation frame, click Allowed Services.
-
Click the Services to Allow drop-down list and select SLP Daemon.
-
Click Add > Next.
-
Click Accept.
-
-
At the command prompt, enter the following command to restart the SLP daemon:
rcslpd restart
-
(Conditional) If you are doing this after installing OES and eDirectory, you must also restart eDirectory by entering the following command:
rcndsd restart
-
Continue with the following sections that apply to your situation:
Synchronizing Data Between OpenSLP DAs and/or Novell SLP DAs
If you didn’t set up DA synchronization during server installation, you can set it up later by using the following parameters in the slp.conf file:
- net.slp.dasyncreg = true/false
- slp.DAaddresses = IP_address_1,IP_address_2
If the net.slp.dasyncreg parameter value is set to true, then synchronization is achieved by the DA pushing or pulling SLP registrations from the DAs listed for the slp.DAaddresses parameter, as follows:
-
When the DA starts up, it pulls the registration information from all of the server DAs listed in the slp.DAaddresses parameter, including any Novell SLP DAs listed.
-
When the DA receives a service registration, it forwards the information to the OpenSLP DAs that are listed.
IMPORTANT:Service registrations cannot be pushed to Novell SLP DA's.
Backing Up Registrations and Managing Persistence
If you didn’t set up registration back-up during server installation, you can set it up later by using the following parameters in the slp.conf file:
net.slp.isDABackup = true/false
net.slp.DABackupInterval = time_in_seconds
If the net.slp.isDABackup parameter is set to true, service registrations are backed up in the /etc/slp.reg.d/slpd/DABackup file at the interval specified for the net.slp.DABackupInterval parameter. By default, the interval is 900 seconds (15 minutes).
Configuring OES Servers to Access the OpenSLP DA
If you created the OpenSLP DA on an OES server installed in your tree, then SLP is properly configured on that server and these instructions do not apply to it.
For all other OES servers installed in your eDirectory tree, you should complete one of the following procedures as it applies to your situation:
Configuring for DA Access During the OES Installation
As you install OES by using the instructions in the OES eDirectory Services
section of the OES 23.4: Installation Guide, do the following:
-
When you reach the
eDirectory Configuration - NTP and SLP
section of the installation, select Configure SLP to Use an Existing Directory Agent.The first option, Use Multicast, requires that you disable the firewall on the server. Disabling the firewall is always discouraged.
-
In the Service Location Protocol Scopes field, specify the scope you defined in Step 4. You can also list additional scopes, separated by commas (no spaces).
For example, you might type Directory in the field if that is the scope name you assigned to the DA you created.
-
In the Configured SLP Directory Agent field, type the IP address of the DA server you defined in Setting Up an OpenSLP DA Server. You can also list additional DA addresses, separated by commas.
-
Return to the
NetIQ Modular Authentication Services
instructions in the OES 23.4: Installation Guide.
Configuring for DA Access Before or After Installing OES
Whether you configure DA access before installing OES server or after install of OES, the manual DA configuration process is the same.
-
Open /etc/slp.conf in a text editor.
-
Find the following line:
;net.slp.useScopes = myScope1, myScope2, myScope3
IMPORTANT:The example in the configuration file is misleading because the spaces after each comma are not ignored as one might expect them to be.
Therefore, the scope names created or configured by the statement after the first comma actually have leading spaces in them. For example, the first scope name is
myScope1
but the scope names that follow it all have leading spaces,myScope2
,myScope3
and so on. This is a problem, especially if one of the later names becomes the first name in a subsequent SLP configuration and the leading space is ignored.If you use the scopes given in the example for some reason, remove the spaces between the entries.
-
Modify the line by removing the semicolon and typing the name or names of the scopes you want this server to have access to. Be sure to include the scope you defined in Step 4.
For example, you might change the line as follows:
net.slp.useScopes = Directory
-
Find the following line:
;net.slp.DAAddresses = myDa1,myDa2,myDa3
-
Modify the line by removing the semicolon and typing the actual IP address of the OpenSLP DA you defined in Setting Up an OpenSLP DA Server.
net.slp.DAAddresses = IP_Address
-
Save the file and close it.
-
At the Linux command prompt, enter the following to restart the SLP daemon and reset its configuration:
rcslpd restart
Configuring NetWare Servers to Use the OpenSLP Service
IMPORTANT:NetWare uses Novell SLP by default and will configure a server for that service if possible.
Complete one of the following as it applies to your situation:
Configuring for DA Access During the NetWare Server Installation
-
In the dialog box where you set up IP addresses for network boards, click Advanced.
-
Click the SLP tab.
-
Specify the IP address of the OES DA servers—up to three.
-
Type the list of scopes covered by the configured DAs that you want the NetWare server to have access to.
IMPORTANT:We recommend you do not configure the server to use multicast because that necessitates disabling firewalls, which is never recommended.
-
Click OK.
Configuring for DA Access After Installing the NetWare Server
-
Using a text editor, edit the SYS:ETC/slp.cfg file on the NetWare server and add the following line for each DA server you want the NetWare server to have access to:
- DA IPV4, IP_Address1
- DA IPV4, IP_Address2
where IP_AddressX is the IP address of an OES DA server.
-
Save the file and close it.
-
At the NetWare console prompt, specify the scopes you want the NetWare server to have access to, write the SLP cache to the registry, and restart the SLP service:
- set slp scope list = scope1,scope2,...
- flush cdbe
- set slp reset = on
-
Verify that SLP is functioning correctly by entering the following command:
display slp services
10.5.4 Using Novell SLP on OES Networks
If you have a NetWare tree, you automatically have Novell SLP on your network and you can continue to use it as the SLP service during the upgrade to OES until you are ready to switch to OpenSLP.
This section discusses the following:
NetWare Is Configured with Novell SLP By Default
When you install NetWare, if you don’t specify an alternate SLP configuration, the server is automatically configured to use Novell SLP in a way that is sufficient for most networks.
Configuring OES Servers to Access the Novell SLP DA
For each of the OES servers installed in your eDirectory tree, you should complete one of the following procedures as it applies to your situation:
Configuring for DA Access During the OES Installation
As you install OES, in the OES eDirectory Services
section of the OES 23.4: Installation Guide, do the following:
-
When you reach the SLP section of the installation, select Configure SLP to Use an Existing Directory Agent.
The first option, Use Multicast, requires that you disable the firewall on the server. Disabling the firewall is always discouraged.
-
In the Service Location Protocol Scopes field, specify one or more appropriate scopes that are defined on your network.
If you aren’t sure about the exact scope names, you can view the SLP configuration of a NetWare server on the same network segment. Log into Novell Remote Manager on the server and click Manage Applications > SLP.
You can list multiple scopes, separated by commas (no spaces).
For example, you might type Directory in the field.
-
In the Configured SLP Directory Agent field, type the IP address of an appropriate DA server.
You can use Novell Remote Manager on a NetWare server if you aren’t sure which address to use.
You can also list additional DA addresses, separated by commas.
-
Return to the
OES eDirectory Services
instructions in the OES 23.4: Installation Guide.
Configuring for DA Access Before or After Installing the OES Server
Whether you configure DA access before installing OES server or after install of OES, the manual DA configuration process is the same.
-
Open /etc/slp.conf in a text editor.
-
Find the following line:
;net.slp.useScopes = myScope1, myScope2, myScope3
IMPORTANT:The example in the configuration file is misleading because the spaces after each comma are not ignored as one might expect them to be.
Therefore, the scope names created or configured by the statement after the first comma actually have leading spaces in them. For example, the first scope name is
myScope1
but the scope names that follow it all have leading spaces,myScope2
,myScope3
and so on. This is a problem, especially if one of the later names becomes the first name in a subsequent SLP configuration and the leading space is ignored.If you use the scope names given in the example, remove the spaces between the entries.
-
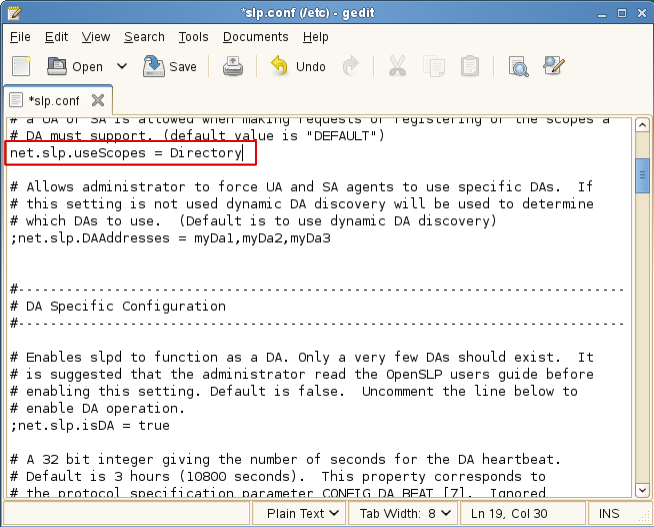
Modify the line by removing the semicolon and typing the name or names of the scopes you want this server to have access to.
If you aren’t sure about the exact scope names, you can view the SLP configuration of a NetWare server on the same network segment. Log into Novell Remote Manager on the server and click Manage Applications > SLP.
You can list multiple scopes, separated by commas (no spaces).
For example, you might change the line as follows:
net.slp.useScopes = Directory
-
Find the following line:
;net.slp.DAAddresses = myDa1,myDa2,myDa3
-
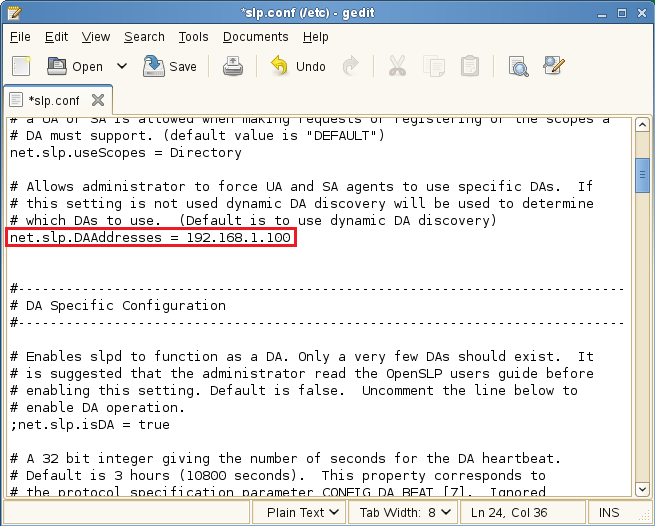
Modify the line by removing the semicolon and typing the actual IP address of the Novell SLP DA (using Novell Remote Manager if necessary).
net.slp.DAAddresses = IP_Address
-
Save the file and close it.
-
At a terminal prompt, enter the following to restart the SLP daemon and reset its configuration:
rcslpd restart
-
Enter the following commands to verify that the DA and scopes you configured are recognized.
slptool findsrvs service:
The DA server should be listed.
slptool findscopes
The scopes should be listed.
-
If you did this after installing OES, enter the following to verify that the tree is found:
slptool findsrvs service:ndap.novell
Checking the Status of Novell SLP Services
There are several ways to check the status of Novell SLP services.
-
If you know the IP addresses of the DAs, check the SYS:\etc\slp.cfg file on non-DA servers to see if the DA IP addresses are listed.
-
If you know the scope names, check for the proper scope name configuration by using the SET SLP SCOPE LIST command.
-
Use the DISPLAY SLP SERVICES command to list all of the services that are registered in all of the scopes that the server is configured to use.
-
Use iManager to open the scope container object to see all of the registered services.
-
If you are registering different services in different scopes, look in the SYS:\etc\slp.cfg file for REGISTER TYPE lines.
-
At the DOS prompt on a Windows workstation with Client32 installed, use the SLPINFO /ALL command.
10.5.5 TIDs and Other Help
The SLP configuration file (etc/slp.conf) is self-documented regarding each of the configuration parameters. OpenText support has also provided the following TIDS:
-
OpenSLP vs. Novell SLP answers questions about the differences between the two SLP solutions.
-
eDir not registering bindery or NDAP services with OpenSLP answers questions about how the SLP solutions register ndap and bindery services.
-
NetWare SLP fails to populate service registrations to an openSLP DA on OES explains how to solve the communication problem.
-
OpenSLP Documentation on the Webprovides complete documentation of the OpenSLP services that OES leverages.