12.11 Mirroring and Cluster-Enabling Shared NSS Pools and Volumes
12.11.1 Understanding NSS Mirroring
NSS mirroring is a checkpoint-based synchronous mirroring solution. Data blocks are written synchronously to multiple storage devices. It is an alternative to synchronous replication options that are provided by a SAN storage array.
Hardware configuration and placement for NSS mirroring can vary depending on geography and fault tolerance requirements. For example, Figure 12-1 depicts a simple hardware configuration in which one side of the mirrored NSS volume is located in a separate building from the rest of the cluster hardware. If a disaster occurs in one building, data is still safe on the mirrored NSS volume in the other building.
Figure 12-1 Single Cluster with Mirrored NSS Volumes in Separate Buildings
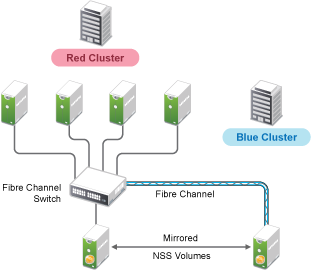
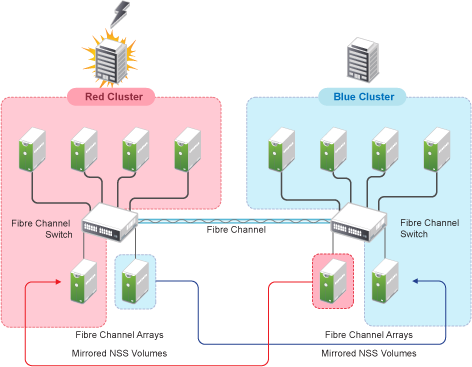
Figure 12-2 depicts a more complex hardware configuration in which two clusters are placed in separate buildings, but each has one side of a mirrored NSS volume in the building with the other cluster. If a disaster occur in one building, data is still safe and immediately accessible on the mirrored NSS volume in the other building.
Figure 12-2 Two Clusters with Mirrored NSS Volumes in Separate Buildings
The maximum distance for a single stretch of fibre without optical repeaters to boost distance is about 10 kilometers. There are various devices available that convert Fibre Channel to IP in order to extend SANs to WAN scale.
NSS mirroring is synchronous, and so mirror I/Os must complete before the next I/O can be sent. Performance is a function of time to do an I/O over the longest link.
12.11.2 Requirements for NSS Mirroring
NSS partitions must be mirrored after they are created. If you have an existing partition that you want to mirror, you can either create another partition of equal size on another device to mirror the first partition to, or let the mirroring software automatically create another partition of equal size on another device.
OES Cluster Services should be installed and running prior to creating and mirroring partitions on shared storage.
When you create a OES Cluster Services system that utilizes shared storage space (a Storage Area Network or SAN), it is important to remember that all servers attached to the shared device, whether in the cluster or not, have access to all of the volumes on the shared storage space unless you specifically prevent such access. OES Cluster Services arbitrates access to shared volumes for all cluster nodes, but cannot protect shared volumes from being corrupted by non-cluster servers.
12.11.3 Creating and Mirroring NSS Pools on Shared Storage
Prior to creating and mirroring NSS partitions on shared storage, ensure that you have the following:
-
OES 2023 is installed on all servers that will be part of the cluster.
-
All servers in the cluster are connected to a shared storage system.
-
One or more drive arrays are configured on the shared storage system.
-
For 512 byte device, at least 20 MB of free space and for 4096 (4Kn) byte device at least 80 MB of free space on the shared storage system for a special cluster partition.
-
To ensure disaster recovery, the device you select to mirror should be in a different storage array.
Use one of the following methods to mirror clustered pool resources:
Creating a Pool on a Shared Mirrored Device
To create an NSS pool resource on a shared mirrored device:
-
Start NSSMU by entering nssmu at the command prompt of a cluster server.
-
Share the devices.
-
Select Devices from the NSSMU Main Menu.
-
Select the two devices that you want to use, then press F6 to mark the devices as Sharable for Clustering.
-
-
Create a mirrored RAID device using the shared devices.
-
Select RAID Devices from the NSSMU Main Menu.
-
Press Insert to create a software RAID, select RAID 1, then press Enter.
-
Use the arrow keys to select the two shared devices that you want to contribute space to the RAID, specify the amount of space to use, then press Enter.
The software RAID device automatically inherits the Sharable for Clustering setting.
-
-
Create a clustered NSS pool on the shared RAID device.
-
Select Pools from the NSSMU Main Menu.
-
Press Insert to create a new pool, then create the clustered pool as usual on the shared software RAID device as described in Section 12.4.2, Creating a Cluster-Enabled Pool and Volume with NSSMU.
-
Mirroring the Partition of an Existing NSS Pool
You can use NSSMU to mirror a clustered pool’s partition. The second device must have as much space available as you know the pool’s real allocated size to be, and be marked as Sharable for clustering. To mirror the partition for an existing clustered NSS pool resource:
-
Start NSSMU by entering nssmu at the command prompt of a cluster server.
-
Share the second device.
-
Select Devices from the NSSMU Main Menu.
-
Select the device that you want to use, then press F6 to mark it as Sharable for Clustering.
To ensure disaster recovery, the device you select to mirror should be in a different storage array.
-
-
Select Partitions from the NSSMU Main Menu.
-
Choose the partition that contains the pool and press F3, enter the RAID name and select the second disk, then press F3 to accept.
This mirrors the existing pool and creates the RAID 1 device where each segment is the size of the pool.
-
Use one of the following methods to initiate mirroring for the newly created mirror:
-
At the terminal console of a cluster node, enter the following to migrate the cluster resource to another node:
cluster migrate cluster_resource destination_node_name
Migrating the pool causes load scripts to be executed and causes the mirroring to start on the new node.
-
At the terminal console of the cluster node where the pool is currently active, enter:
dmsetup message raid_device_name 0 remirror=onWARNING:Issue this command only on the node where the pool is currently active. Issuing the command on multiple nodes can corrupt the mirror.
-
-
Verify that the remirroring has begun by opening NSSMU on the node where the pool is currently active, open the RAID page, then select the RAID device.
The remirroring status shows a percentage that is greater than 0. It is fully synchronized at 100%.
12.11.4 Verifying the NSS Mirror Status in the Cluster
After you have configured NSS mirroring with OES Cluster Services, you should check to ensure that it is working properly in a cluster environment.
-
Ensure that the volumes on the cluster-enabled pool are mounted on an assigned server by entering nss /volumes at the terminal console.
-
Check the mirror status of the mirrored partition by entering nlvm raid status at the terminal console of the server where the NSS pool on the mirrored partition is active.
After entering nlvm raid status, you should see a message indicating that mirror status is 100 percent or a message indicating that the mirrored object is fully synchronized.
-
Migrate the pool to another server in the cluster and again check to ensure that the volumes on the pool are mounted by entering volumes at the terminal console.
-
Check the mirror status of the partition again by entering nlvm raid status at the terminal console.