1.4 BCC Deployment Scenarios
There are several Business Continuity Clustering deployment scenarios that can be used to achieve the desired level of disaster recovery. Three possible scenarios include:
1.4.1 Business Continuity Cluster Solution
The business continuity cluster deploys two independent clusters at geographically separate sites. The clusters can be designed in one of two ways:
-
Active Site/Active Site: Two active sites where each cluster supports different applications and services. Either site can take over for the other site at any time.
-
Active Site/Passive Site: A primary site in which all services are normally active, and a secondary site which is effectively idle. The data is mirrored to the secondary site, and the applications and services are ready to load if needed.
The active/active deployment option is typically used in a company that has more than one large site of operations. The active/passive deployment option is typically used for the purpose of disaster recovery when the primary site get lost. Replication of data blocks is typically done by SAN hardware, but it can be done by host-based mirroring for synchronous replication over short distances up to 10 km.
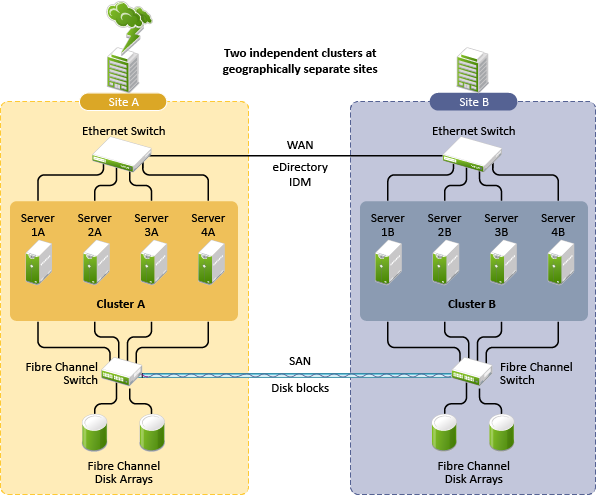
1.4.2 Two-Site Business Continuity Cluster Solution
The two-site business continuity cluster deploys two independent clusters at geographically separate sites. Each cluster can support up to 32 nodes. The clusters can be designed in one of two ways.
Figure 1-3 shows a two-site business continuity cluster that uses storage-based data replication between the sites. BCC uses eDirectory and Identity Manager to synchronize cluster information between the two clusters.
Figure 1-3 Two-Site Business Continuity Cluster
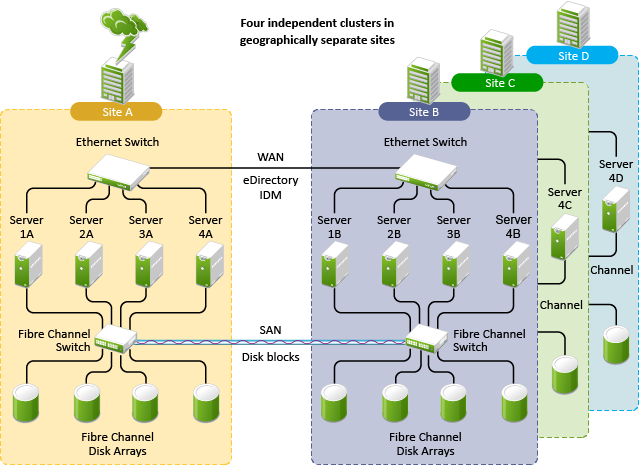
1.4.3 Multiple-Site Business Continuity Cluster Solution
The multiple-site business continuity cluster is a large solution capable of supporting up to four sites. Each cluster can support up to 32 nodes. Services and applications can do fan-out failover between sites. Replication of data blocks is typically done by SAN hardware, but it can be done by host-based mirroring for synchronous replication over short distances up to 10 km.
Figure 1-4 depicts a four-site business continuity cluster that uses storage-based data replication between the sites. BCC uses eDirectory and Identity Manager to synchronize cluster information between the two clusters.
Figure 1-4 Four-Site Business Continuity Cluster