Configuration
Common configuration for all Enterprise Server Cluster members
All members of an Enterprise Server Cluster, including the Global Lock Manager (GLM), must have the JES subsystem enabled
and share the same system catalog and Data Allocation Default Location (DADL). These settings are typically defined on the
JES tab of a region definition.
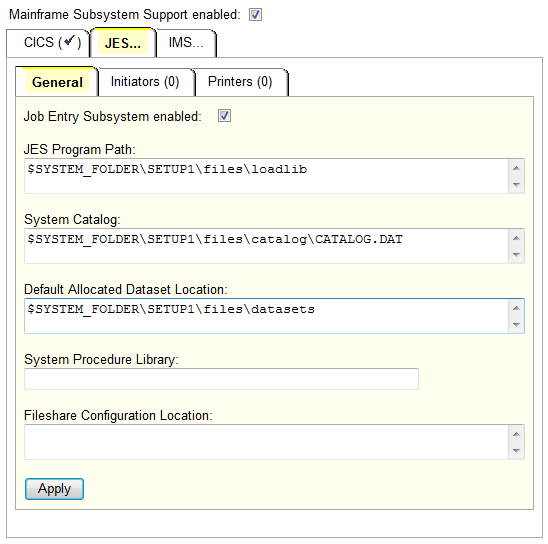
These settings are verified during the handshake between each Enterprise Server Cluster client and the Enterprise Server GLM. The location and name must match for all regions in the cluster. If a mismatch is found, the following message is sent to the console.log:
TXSI5014S Severe error in ES cluster negotiation with parm 1 (parm 2), region terminating
The message will further display whether the mismatch was discovered in the CATALOG.DAT location or the DADL.
Following a successful handshake, the message:
CASSI5012I Successfully negotiated with ES Cluster manager GLMAPPLID
is displayed in the console.log.
- ES_CLUSTER
- Cluster members identify themselves by checking the existence of environment variable ES_CLUSTER in their environment space. Any value sets the variable - e.g. ES_CLUSTER=YES.
Configuring the Enterprise Server Cluster GLM
- ES_GLM
- The GLM identifies itself by checking the existence of environment variable ES_GLM in its environment space. Any value sets the variable - e.g. ES_GLM=YES.
- ES_GLM_TIMEOUT=60
- This environment variable can be set on the GLM only. From this value, defined in seconds, the system will derive the number of retries made to the GLM if a communication error is encountered before the status of the connections to the Enterprise Server Cluster is marked as Disabled. The value set on the GLM is pushed to all clients.
Configuring Enterprise Server Cluster members
There is no further configuration required for an Enterprise Server Cluster member.
- It shares its system catalog and DADL with all members of the cluster.
- It sets a value for the environment variable ES_CLUSTER.
- The GLM is started prior to this server instance, or a file called CASGLM.LCK already exists and contains a list of the Enterprise Server Cluster members and their state - active or inactive.
Configuring dataset scope
- Name: ESCLRNLs.cfg
- Location: Create the ESCLRNLs.cfg file in the same folder as that used by the system catalog.
RNLDEF RNL(INCL)TYPE(GENERIC) QNAME(SYSZDSN)This will result in a global scope set for all SYSZDSN.
ISC listeners and SYSC connections
Cluster members communicate over the Micro Focus ISC interface. Dynamically-created ISC listeners and ISC connections are activated between each Enterprise Server Cluster client and the Enterprise Server Cluster manager. There are no requirements to define ISC listeners and/or SYSC connections. The information required to create the ISC resources is collected dynamically and stored in the CASLGM.LCK file by the GLM, and later consumed by all members of the Enterprise Server Cluster.
ISC-based connections will be identified by APPLID and SYSID, therefore APPLIDs and SYSIDs must be unique throughout the system.
The APPLID is derived from the Enterprise Server name, so it's simple to ensure that all Enterprise Cluster members have different names.
The SYSID is defined in the System Initialization Table (SIT). Each Enterprise Server Cluster member will require its own SIT. The same resource definition file can be used across the whole Enterprise Server Cluster.