This topic describes the editing features for the various file types used in your project.
Note: We recommend that you create backup copies of all files before you start editing them.
Editing COBOL Files
You are going to explore some of the COBOL editing features using the
ZBNKPRT1.cbl program which produces a report from a sequential data file.
- In Solution Explorer, double-click
ZBNKPRT1.cbl.
This opens the file in the COBOL editor in Visual Studio.
- Expanded Copybook View
-
- Scroll down the file to line 005000 and see some COPY statements.
- Right-click the line for
COPY CDATED and click
Show "CDATED".
This expands the copybook directly in the code of
ZBNKPRT1.cbl.
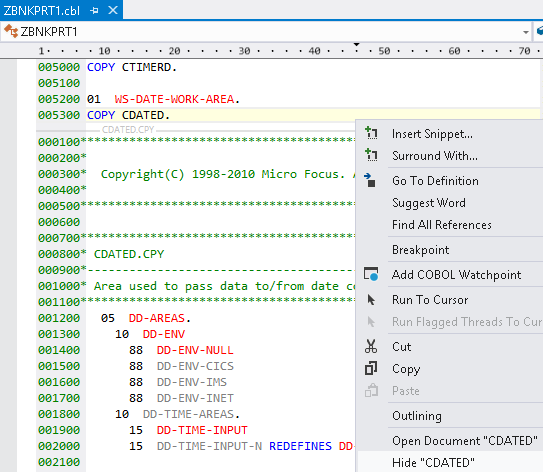
- You can edit the code of the copybook in the expanded view so introduce an error in the code now.
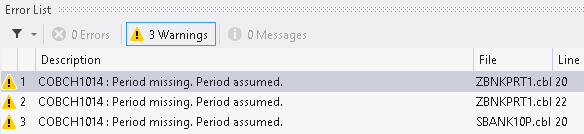
This automatically outputs messages in the Error List window about problems that occurred in the code. You can sort the list by file name. Double-clicking the line for an error in the Error List window positions you on the line in the copybook in the expanded view which causes the error.
- Close the file.
The changes you made to the expanded view were applied to the source of the copybook so now you are prompted to save the file - click
No.
- Unused data
- Notice that some data items in the Data Division are greyed out. This is because they are not referenced in the Procedure Division.
- Class View
- You can view the objects and the members defined in your projects in the standard Class View located in the tabbed window at the top right of the IDE:
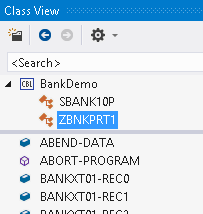
If this window is closed, you can open it from
.
- Navigation in the code
- Apart from scrolling down the code in the editor, you can use the following features of the IDE:
- Use the drop-down menus at the top of the editor:
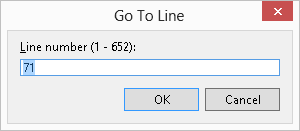
- In Solution Explorer double-click on
DBANK52P.cbl to open the file, and then click on
to navigate to a certain line in the code.
- Click
and start typing a search term:

- Exploring data in editing mode
-
- Open the
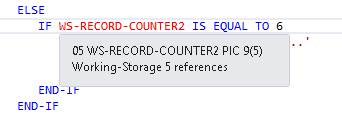
ZBNKEXT1.cbl file, and scroll down the code to line 24700.
- Hover over the
WS-RECORD-COUNTER2 data item.
This provides you with details of the location, the size, the format, and the number of times the field is used in the program.
- Data definitions
-
- Right-click a data item in the Procedure Division and click
Go To Definition.
This positions the cursor on the line of code where the data item is defined.
- Finding all lines where a data item is used
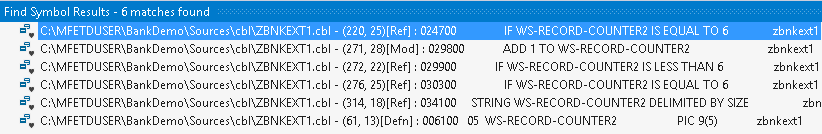
-
- Right-click a data item in the code, and click
Find All References.
This opens the Find Symbol Results window with a list of all occurrences of the data item in the code.
- Searching in copybooks
- You can search for strings in the copybooks as follows:
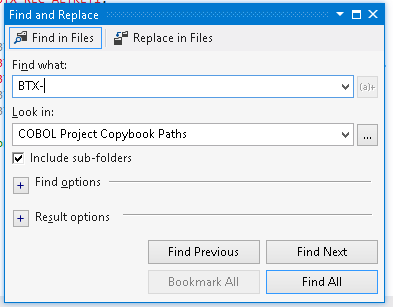
- Click
Edit > Find and Replace > Find in Files.
- Set the
Look in to
COBOL Project Copybook Paths.
- Type
BTX- in the
Find what field.
- Click
Find All.
The results are displayed in the
Find Results 1 window.
- Marking text and block mode
- You can use the mouse to mark the text. To make a block selection of the code:
- Press
Alt and drag the selection with the mouse.
- Smart editing
- Let's look at is Smart Editing with background COBOL parsing:
- Scroll down to line 25000 in the ZBNKPRT1.cbl file and start typing the following, starting in area A of the code, one character at a time:
MOVE W TO
Notice how the words you type change in the editor. Once a word is recognized as a reserved word or a data item, its color changes. If a line of code contains invalid COBOL syntax, the word that is not recognized is underlined with a wavy red line. You can check the Error List window to see what errors are reported.
- Change the line to:
MOVE 34 TO WS-
- If you have changed this COBOL program, copy the backup version back in again.
- Renumbering the COBOL sources
- You can use the commands
Renumber and
Unnumber to insert and remove line numbers from your code. Your sources include some comments beyond column 73, so you need to configure the line numbering in order to ensure you only apply changes to the COBOL sequence area:
- Click
Tools > Options > Text Editor > Micro Focus COBOL > Line Numbering.
- Ensure that only the
COBOL (left margin) option is enabled and that
Standard (right margin) is disabled.
- Click
OK.
You can now remove the line numbers from your code - note that the
Renumber and
Unnumber commands are not available in the expanded copybook view.
- Right-click the
ZBNKPRT1.cbl file in the editor, and click
Unnumber.
This removes the line numbers from the COBOL sequence area.

To reinsert the line numbers in your code:
- Right-click the
ZBNKPRT1.cbl file in the editor, and click
Renumber.
To insert line numbers beyond the end of area B:
- Click
Toggle Standard line numbering mode
 on the COBOL toolbar to quickly enable the standard line numbering - this is equivalent to enabling
Standard (right-hand margin) in the IDE options.
on the COBOL toolbar to quickly enable the standard line numbering - this is equivalent to enabling
Standard (right-hand margin) in the IDE options.
- Right-click the
ZBNKPRT1.cbl file in the editor, and click
Renumber.
You should now see line numbers running down both sides of the source code:
- Click
Edit > Undo to revert your changes to the file.
JCL editing
- Double-click the JCL file in Solution Explorer to open it in the JCL editor.
The editor lets you edit JCL files in text view and offers a basic level of colorization for items such as reserved words and comments. The JCL editor does not support background parsing or syntax checking.
BMS editing
There are two ways to edit BMS files. The first one is to use the basic BMS text editor available in the IDE. The other is to use a WYSIWYG version, the
Micro Focus BMS Painter, which is available as a separate utility installed with this product.
To open the BMS file in the IDE text view:
- In Solution Explorer, double-click
MBANK10.bms to open it in the basic BMS editor.
Although you can use this basic text editor to make small changes, it is quite difficult to edit BMS files in text view.
A much more suitable and less error-prone way to edit BMS files is to use the BMS Painter.
-
In Solution Explorer, right-click
MBANK10.bms and click
Open BMS Painter.
This starts the external
Micro Focus BMS Painter.

- In BMS Painter, you can click fields and move them by dragging.
For example, double-click the data field immediately following the text “User Id” and move it to a different position on the map.
- To add a field, click in the desired place in the window and start typing.
- To change a field's properties, right-click it and select
Properties.
- To change the properties of the map or mapset, right-click the item and select
Properties.
For example, do this for the MBANK10 mapset and the BANK10A map.
- Click
to close the utility and do not save the file.
Editing data files
You can edit data files using one of two available
Micro Focus Data File Editor tools.
- In Solution Explorer, right-click the .dat file and click
Open File in Data Tools.
- The
Classic Data File Editor opens the data file and shows two views:
- The left-hand pane shows the raw form of the file. Because many of the field are COMP-3 fields, the data in these fields is presented in an ASCII view.
- The right-hand pane shows the record layout for the file in its detailed field view and the COMP-3 fields are shown in a much better, editable form.
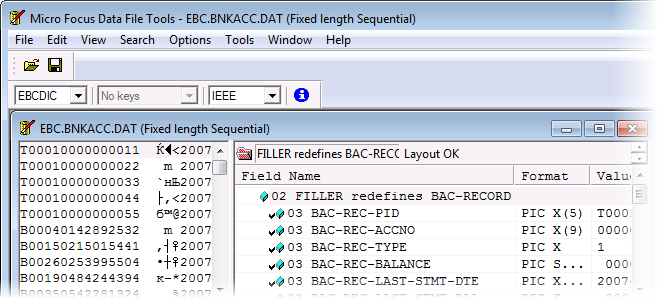
- Change the value of BAC-REC-BALANCE from 91.14 to 132.76 as follows:
- Double-click in the
Value field for BAC-REC-BALANCE. You may get an
Update warning dialog box when you start typing the new value.
- Click
Yes to confirm you want to make changes.
- Position the cursor in front of the third number before the decimal point and start typing.
- Press
Enter to confirm the change.
- Close the Classic Data File Tools utility without saving your changes.






 on the COBOL toolbar to quickly enable the standard line numbering - this is equivalent to enabling
Standard (right-hand margin) in the IDE options.
on the COBOL toolbar to quickly enable the standard line numbering - this is equivalent to enabling
Standard (right-hand margin) in the IDE options.



