AWM is a framework based on EMF which lets you create a model to support the application development process within an Eclipse-based environment.
The original aim of AWM was to support the development process on a z/OS mainframe. Over the years, the mainframe development tools have frequently been increasingly adapted to the needs of the developer. Home-grown user interfaces, as well as complex compile and release procedures, mean that the change to a modern development framework based on Eclipse has become an extensive project.
AWM's aim has now been extended to support the creation of models for any Eclipse-based application development process.
With AWM, the effort of integrating existing remote and local development tools in Eclipse, and the future maintenance of the tool integration is considerably simplified. AWM has been designed so that, where required, the existing development procedures and tools can be integrated in Eclipse with minimum effort. The tool attachment is based on a model-driven approach. With the help of an AWM model editor, an XML file will be edited by an administrator. At run time, the AWM model will be dynamically integrated under Eclipse, and that supports both the modeled user interface and the modeled tool attachment.
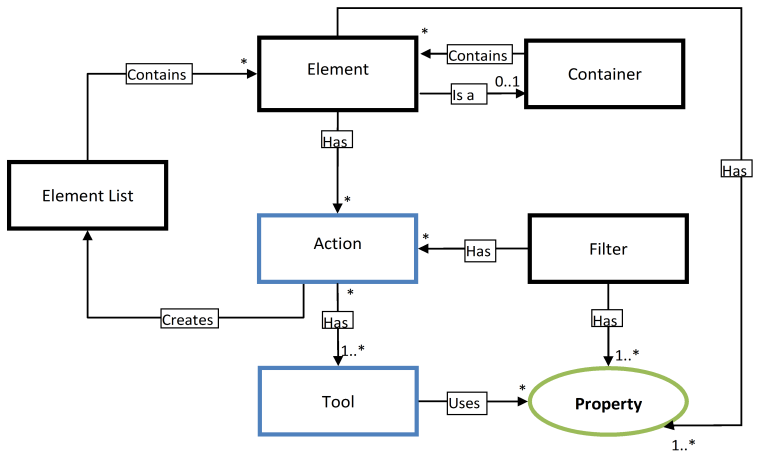
AWM uses the following general expressions to describe the tool integration as flexibly as possible:
A complete Eclipse-based user interface for the integration of tools can be described with the help of the AWM model editor and the expressions defined above.
Several Elements can be identified in an SCM system. Elements can either represent the files managed by the SCM system or Containers in which the files are structured, such as projects, stages, and folders.
All elements have Properties. A property is an attribute of a type and is assigned a value at run time, for example file name.
Tools, on the other hand, use properties as input parameters and assign properties to their output parameters. Tools are components of Actions to which elements can be assigned. Examples include Check-out, Edit, Compile, Delete.
A Delete tool, for example, requires the file name of the file to be deleted as an input parameter. The file exists as an Element, and has the property “File name”. The tool is modeled in the AWM model so that it uses the “File name” property as an input parameter. Used on an element, its file name will be transferred to the tool, and the file will be deleted.
You can define the elements that he would currently like to work with, using Filter at run time. The criteria by which elements can be searched can be entered in the filter. The corresponding elements can be returned via an action. Returned elements are managed in element lists.
All the object types are shown below: