





If you do not want users to have a mainframe connection when working with the Workflow Manager for the first time (or at all), they can use a local master configuration file (or default configuration).
A local master configuration file can either be located in the Eclipse root folder with the name MasterConfig.xml or MasterConfig.txt depending on its format (see Master configuration syntax below) or be returned by a local operating system command (see Master Configuration). If that is the case, a local system reference can be created in the Team Developer Tree View by using the "Add System(s) ..." function and selecting the "Local System" entry in the dialog that is displayed. When expanded, the local system reference should contain all the applications defined in the local master configuration file.
If any application of a local system reference contains mainframe-dependent actions, or the model of one of the applications is stored on the mainframe, you must add the mainframe connection to the local system reference, by right-clicking the local system reference and selecting "Associate Remote System…" (see the figure below).
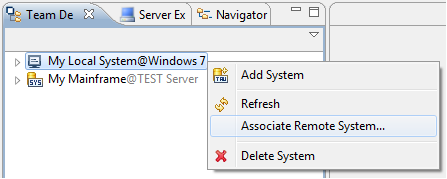
After the association has been made, the label of the local system reference changes and the Properties view shows properties of the selected remote system. The context menu now also shows the function "Remove Associated Remote System". A local system reference with an associated remote system acts just like a remote system reference, except the local master configuration is not provided via the mainframe.
The master configuration can be defined in one of two supported formats: flat format and XML. The XML format is currently only supported by local system references, meaning that master configuration files located on the mainframe must be defined in flat format. Both formats use the same keywords. The table below shows all available keywords and their meanings.
The flat format master configuration consists of lines with keywords, together with the respective values. The keywords are separated from the values by a colon and at least one space.
As an example, a row in the master configuration file will look like this:
System: System_nameLines beginning with an asterisk (*) are interpreted as comments.
Any number of modeled applications can be listed for a system. The master configuration file must have at least one application defined.
The Conf entry consists of the specification of the platform together with the platform-dependent fully-qualified or absolute file name. Permissible platform designations are local and mvs.
The INFO entry determines which persistent information held in the Eclipse Workspace will have to be deleted in the case of a version change of the modeled application, for consistency. Permitted information is filters and elements. The information can be combined in any way.
| INFO entry | Deleted files | Content of the files |
|---|---|---|
| filters | ft_filters.xml | All filters in the application |
| elements | et_elements.xml | All cached elements that are assigned to the application and all element lists in the application |
Sample for a master configuration file in XML format:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <System name="My Local System"> <Appl name="My Application" conf="local:C:\Models\MyApplication.model" version="1.0" info=""> <Property propertyID="PROP_UserRole" value="ADMIN" /> <Property propertyID="PROP_Environment" value="TEST" /> </Appl> <Appl name="SCLM Application" conf="MVS:HLQ.APPLS.MODELS(SCLMPROD)" version="2.1" info="" /> </System>
Sample for a master configuration file in flat format:
System: My System * * PDS EXPLORER EXAMPLE APPLICATION * User: * application name Appl : PDS Explorer * location of the application configuration file Conf : mvs:'hlq.ZSERVER.XML(PDSECONF)' * application version number Version: 1.1 * process information
A local master configuration can be returned dynamically by an operating system command. The command, which could, for instance, execute a script file to return the configuration, must be specified with the "teamdeveloper.masterconfig" Java system variable (see Setting Java System Variables).
The value of the variable must contain an operating system command, which returns a complete master configuration file in XML format to standard out when executed.


