5.16.7 Service Provider Brokering
The Service Provider Brokering (SP Brokering) feature enables Identity Server to act as a federation gateway or a service provider broker. This federation gateway allows you to connect to different protocols such as Liberty, SAML 1.1, and SAML 2.0.
You can use SP Brokering with the Intersite Transfer service of the identity provider. Intersite Transfer service enables authentication at a trusted service provider. SP Brokering helps companies establish trust between identity providers and their service providers that support different federation protocols. For example, an identity provider that supports SAML 2.0 can provide authentication to a Liberty or SAML 1.1 service provider by using SP broker.
SP Brokering helps reduce the number of trust relationships between an identity provider and their service provider. For example, identity providers can now provide authentication to their service providers by establishing a single trust relationship instead of multiple trust relationships. Similarly, a service provider must establish a single trust relationship with SP Broker to receive authentication from several identity providers.
You can control the authentication flow between several identity providers and service providers in a federation circle by allowing the administrator to configure policies that control Intersite Transfers. For example, an administrator can configure a policy with SP Broker that allows only certain users from an identity provider to be authenticated at a given service provider.
An Intersite Transfer URL has the following format: https://<identity provider>/idpsend?PID=<Service Provider ID>&TARGET=<final_destination_URL>
This Intersite Transfer URL consists of three parts:
-
https://<identity provider>: The user can authenticate at the identity provider.
-
/idpsend?PID=<Service Provider ID>: Authentication occurs at the service provider represented by the service provider ID at the identity provider.
-
&TARGET=<final_destination_URL>: The user is finally redirected to the specified target URL associated with the service provider.
A web page is created with many Intersite Transfer URLs for each combination of identity provider, service provider, and the target application. See Using the Intersite Transfer Service.
The following illustration explains the SP Brokering flow of granting access to the target URL:
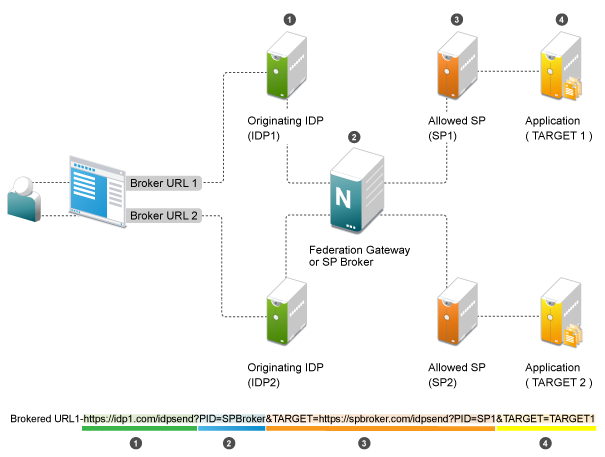
Web Page (User Portal): A web page (user portal) is created with a list of URLs called Brokered URLs, which provide access to various target applications.
Originating Identity Providers: The Originating Identity Provider is the identity provider with which the user credentials are stored for authentication. The Origin IDP must be configured as a Liberty/SAML1.1/SAML2.0 trusted identity provider in the SP Broker.
Federation Gateway or SP Broker: The Federation Gateway or SP Broker is a Access Manager identity provider that can be configured to control the authentication between several Origin IDPs and Allowed SPs in a federation circle.
Allowed Service Provider: The Allowed SP is the service provider in which the SP Broker provides authentication. The allowed SP must be configured as a Liberty/SAML1.1/SAML2.0 trusted service provider on SP Broker.
Target Application: The target application is the application running on a web sever that is protected by the service provider.
Broker URL: A Broker URL is a specially designed Intersite Transfer URL, which consists of four parts. You can click the brokered URL, which results in the following:
-
You must authenticate with the Originating IDP (https://idp1.com/idpsend).
-
The Origin IDP causes an authentication to occur at the SP Broker (?PID=SPBroker).
-
The SP Broker causes an authentication to occur at the allowed SP (TARGET=https://spbroker.com/idpsend?PID=SP1).
-
You are redirected to the target application (?TARGET=TARGET1).
SP Brokering requests are the Intersite Transfers resulting from brokered URLs processed on the SP Broker. The SP Broker can control the brokering requests before providing an authentication to the service provider. The SP Broker enforces the policies configured by the administrator by either causing the authentication at the service provider or by denying the request.
The SP Broker provides the following options to configure policies that control SP brokering requests:
-
A set of SAML 1.1, SAML 2.0 and Liberty trusted identity providers and trusted service providers can be configured as a brokering group. The brokering request is allowed only if the Origin identity provider and Allowed service provider belong to the same brokering group. Brokering Request is not allowed from an Origin identity provider of one group to an Allowed service provider of another group.
-
In a brokering group, a set of brokering rules can be configured that provides granular control on the brokering requests. For example, a brokering rule can be configured to deny a brokering request from an Origin identity provider to an Allowed service provider, if the user satisfies a certain condition at the SP Broker.
SP brokering is enabled on Identity Server only if at least one brokering group is enabled. If an Intersite Transfer request is received with neither the origin identity provider nor the Allowed service provider in any of the brokering group, the request is treated as a regular Intersite Transfer and SP brokering controls are not applied.
-
Configuring a Brokering for Authorization of Service Providers
-
Generating the Brokering URLs by Using an ID and Target in the Intersite Transfer Service
-
Assigning the Roles for the Origin IDP users in SP Broker Using the Transient Federation Attributes
-
Assigning the Local Roles Based on Remote Roles and Attributes