Identity Providers and Consumers
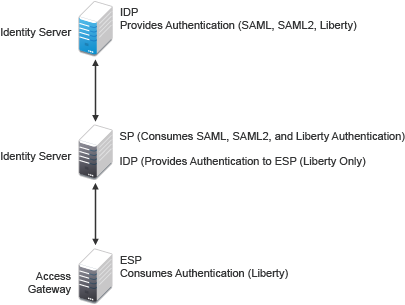
An Identity Server can be configured as an identity provider, which allows other service providers to trust it for authentication. It can also be configured as a service provider, which enables Identity Server to consume authentication assertions from trusted identity providers. Figure 2-17 depicts two Identity Servers. Identity Server at the top of the figure is configured as an identity provider for SAML 1.1, SAML 2.0, and Liberty authentication. Identity Server in the middle of the figure is configured as a service provider, consuming the authentication credentials of the top Identity Server. This second Identity Server is also configured as an identity provider, providing authentication for the Embedded Service Provider of Access Gateway.
Figure 2-17 Identity Server Trust
As an administrator, you determine whether your server is to be used as the identity provider or service provider in the trust relationship. You and the trusted partner agree to exchange identity provider metadata, and then you create references to the trusted partner’s identity provider or service provider in your Identity Server configuration. You can obtain metadata via a URL or an XML document, then enter it in the system when you create the reference.