1.6 Deploying Access Manager on Public Cloud
The following list provides the recommended configuration details for deploying Access Manager on Amazon Web Services (AWS) EC2 and Microsoft Azure:
-
Install the LDAP server and Administration Console in the private subnet. Both of these contain a permanent store of sensitive data. Install web servers also in the private subnet for added protection.
In the private subnet, servers do not have any public IP address. This prevents the servers from security vulnerabilities. However, the servers on the public subnet can have public IP addresses.
-
You cannot access Administration Console directly in the private subnet. Therefore, it is recommended to configure a dedicated server called as jump server in the public subnet. You can then use the jump server to access Administration Console. You can use a Windows server as a jump server and Remote Desktop Protocol to access the jump server.
For more information about jump servers, see Linux Bastion Host Quick Start.
-
The cloud-based service provider routes communications among servers on the public subnet and servers on the private subnet.
-
Install Identity Server in the public subnet because it does not permanently store any sensitive user data.
This configuration has been tested with a load balancer to support clusters of Identity Server and Access Gateway. As the number of users and demands for web resources increase, you can easily add another Identity Server or Access Gateway to handle the load. You can then add the new servers to the load balancer. When new servers are added to the cluster, they are automatically sent the cluster configuration. See Recommendations for Scaling Access Manager Components in Public Cloud.
The following sections provide information specific to AWS EC2 and Microsoft Azure:
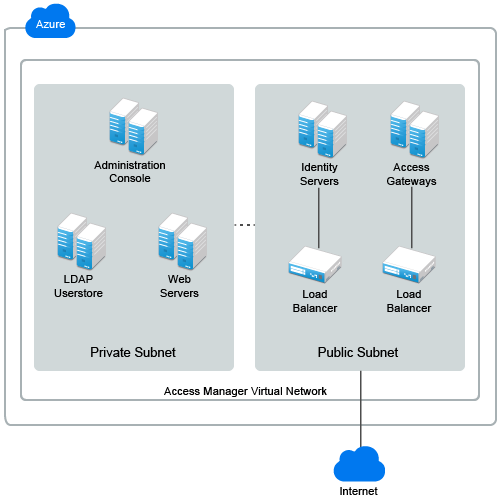
1.6.1 Deploying on AWS EC2
You need to configure a VPC NAT gateway. Servers in the private subnet use VPC NAT gateway to access the Internet. Similarly, you need to configure an Internet gateway for enabling servers in the public subnet to access Internet and vice versa. For more information, see the Amazon Virtual Private Cloud Documentation.
For more information about AWS EC2 VPC, see Amazon Virtual Private Cloud Documentation.
For information about how to deploy Access Manager on AWS EC2, see ‘Deploying Access Manager on Amazon Web Services EC2.
Figure 1-7 Access Manager Deployment on AWS EC2
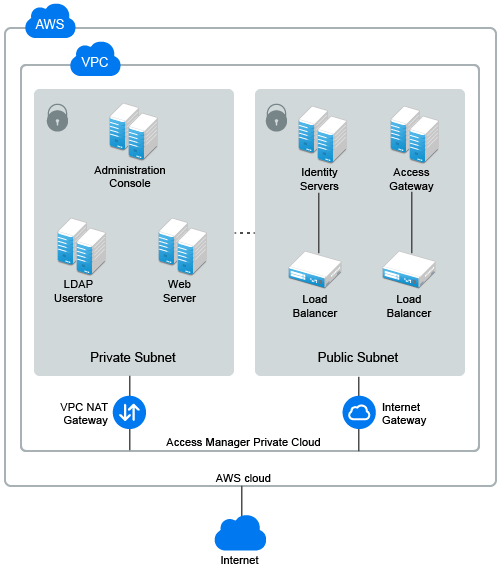
1.6.2 Deploying on Microsoft Azure
In Microsoft Azure, you do not need to configure a VPC NAT gateway and Internet gateway. Azure takes care of this configuration.
For more information about the Azure virtual network, see Virtual Network Documentation.
For information about how to deploy Access Manager on Azure, see Deploying Access Manager on Microsoft Azure.
Figure 1-8 Access Manager deployment on Microsoft Azure