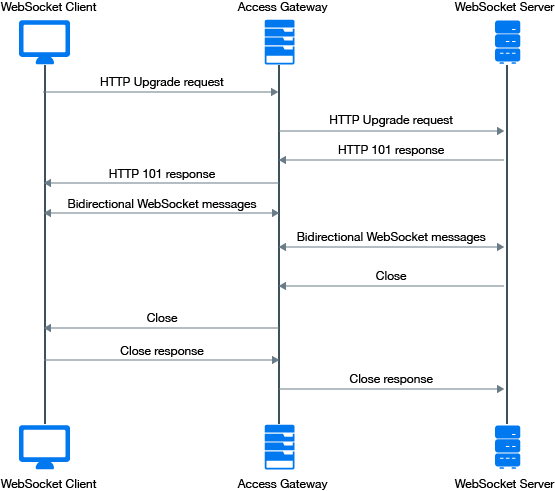
2.7.2 WebSocket Support
The WebSocket protocol is an extension to the HTTP 1.1 protocol to enable two-way communication between a client and a server. It is an independent TCP-based protocol. It has two parts: handshake and data transfer. HTTP servers interpret its handshake as an upgrade request. By default, it uses port 80 for regular WebSocket connections and port 443 for WebSocket connections tunneled over Transport Layer Security (TLS).
Workflow:
-
A client sends an HTTP upgrade request to the server through Access Gateway to establish a communication channel between the client and the server. (WebSocket protocol handshake)
-
The server sends an HTTP 101 response to the requesting client through Access Gateway. When the client receives the response, the HTTP connection is upgraded to WebSocket.
-
Bidirectional data exchange happens between the server and the client over the WebSocket connection.
-
Any participants in the data exchange can request to terminate the WebSocket connection. When a participant sends a close request to other, the connection is terminated.
WebSocket enables Access Gateway to accept an HTTP upgrade request from a client.
Figure 2-7 illustrates the flow of messages among the client, Access Gateway, and the server in a WebSocket communication.
Figure 2-7 WebSocket Communication