The FREE statement frees up dynamic storage that was previously allocated by an ALLOCATE statement.
General Format
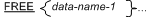
General Rules
- If data-name-1 identifies the start of storage currently allocated by an ALLOCATE statement, the storage is released and data-name-1 set to NULL.
- The length of the released storage is the same as the length allocated using the ALLOCATE statement, and so the contents of any data items within the storage become undefined.
- If data-name-1 contains a predefined address of NULL or an address of storage not allocated via the ALLOCATE statement, no storage is freed. The pointer data-name-1 will be kept unchanged, and behavior is undefined.
- If more than one data-name-1 is specified in a single statement, the effect is as if individual FREE statements were entered, in the order in which the data-name-1 pointers are specified.
Syntax Rules
- data-name-1 must be defined as USAGE IS POINTER.
- data-name-1 can be qualified or subscripted.








