16.2 MFA Server Architecture
Figure 16-1
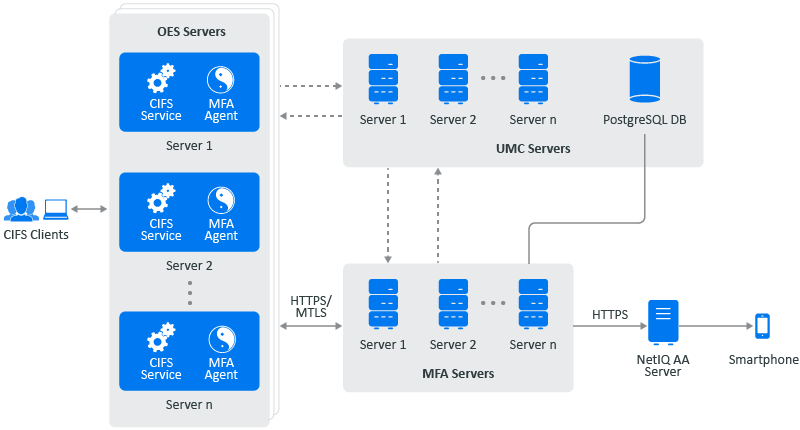
-
MFA servers: One or more centralized servers configured in the eDirectory tree provides MFA service. While a single MFA server is sufficient for MFA functionality, additional servers can be configured for high availability. All MFA servers must reside within the same eDirectory tree.
-
MFA agent: The MFA agent is installed and active on the OES servers that require the MFA service. MFA agents must reside within the same eDirectory tree as the MFA server. In this release, the MFA agent is operational on all CIFS servers.
-
Database: The OES MFA server uses the UMC database, and no additional configuration is required.
-
UMC server: The OES MFA service relies on UMC for database and service discovery. With service discovery, MFA agents discovers the available MFA servers and store address of the servers in the configuration file.
-
OES Services: The OES services that utilize the OES MFA service for multifactor authentication are currently limited to the CIFS service in this release.
-
AA server:OES MFA service uses NetIQ Advanced Authentication server in the back-end for multifactor authentication. Smart phone push is the only authentication method supported as of now.
16.2.1 MFA Control Flow Diagram
Figure 16-2 MFA Control Flow Diagram

The CIFS client initiates a request to map a network drive to the CIFS server. The CIFS server authenticates the user against Active Directory (AD) or eDirectory. After successful user authentication, the CIFS server sends a request to the MFA agent to perform multifactor authentication for the user.
The MFA agent forwards the authentication request to the MFA server, which in turn forwards it to the Advanced Authentication (AA) server. The AA server triggers the second factor authentication (smart phone push) and sends the result back to the MFA server, then to the MFA agent, and finally to the CIFS server. The CIFS server then sends a response back to the CIFS client, indicating whether the authentication was successful or failed.
Each successful MFA authentication session is stored in the database.