Interfaces
Context:
Program Structure Types
interface-specification
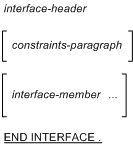 |
interface-header
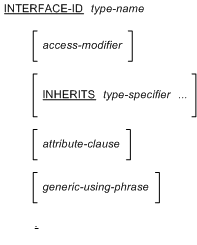 |
interface-member
 |
Example
*> Interface definition
interface-id IClock
01 Hour binary-long property with no set.
01 Minute binary-long property with no set.
method-id Reset.
end method.
end interface.
*> Extending an interface
interface-id IAlarmClock implements type IClock.
01 AlarmHour binary-long property.
01 AlarmMinute binary-long property.
method-id Snooze (#time as binary-long).
end method.
end interface.
*> Interface implementation
class-id WristWatch implements type IAlarmClock,
type System.IDisposable.
working-storage section.
01 Hour binary-long property with no set.
01 Minute binary-long property with no set.
01 AlarmHour binary-long property.
01 AlarmMinute binary-long property.
method-id Dispose.
invoke self::Reset()
end method.
method-id Reset.
set Hour to 0
set Minute to 0
set AlarmHour to 0
set AlarmMinute to 0
end method.
method-id Snooze (#time as binary-long).
add #time to AlarmMinute
end method.
end class.
About Interfaces
An interface is a list of instance methods specifying names and signatures but without implementation.
When a program declares that it implements a particular interface this means that the program is required to have implementations for all the methods defined in the interface. To implement an interface you use the IMPLEMENTS phrase of the OBJECT clause in a class definition to declare that a program provides an implementation for the specified interface. You can also declare an object reference to this interface type.
A Java interface may also include static methods, and these can be accessed directly as for any other static method; for example: if an interface MyInterface includes a static method Static1 with a string parameter, you can code:
invoke type MyInterface(“Hello”)
However, it is not currently possible to define a static method inside a COBOL interface.