Linked resources
To 'link' a folder to your project, click File > New > Folder to display the New Folder dialog box. Click Advanced, select Link to alternate location (Linked Folder), and then navigate to the folder that you want to link to.
Here are some examples of when you need to use linked resources:
Copybooks that are not stored in the project
To access COBOL copybooks outside of the project, you must use linked folders, rather than link to the individual files.
Existing source structures
If you have an existing structure of sources that does not match the Eclipse model of one project per folder, you might find that linked resources are the best solution.
Linked resources enable you to use the sources without having to move them or co-locate them with the project files. You can even set the output folder to be a linked folder, so that your build artifacts could be located somewhere outside the project.
Using linked resources with project or workspace variables
You can specify the location as an absolute path, but this might not be convenient if multiple users on separate machines work on the same project shared though a source control system. In such cases, it is helpful to configure project or workspace variables.
For example, consider the following file system:
/root-folder /checkout-folder/ /shared_files /project
Where the folders shared_files and project contain the sources for your application.
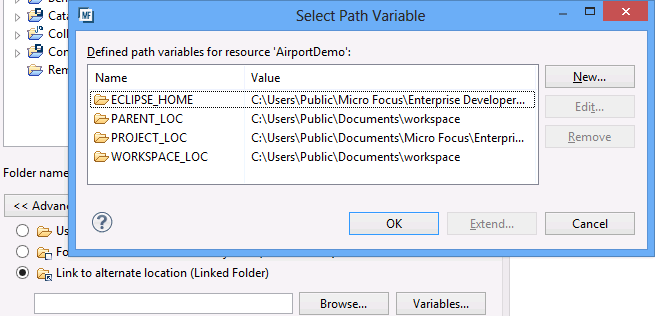
Different users could check out the sources (shared_files and project) under a different directory structure on their local machines. This means if the project itself needs to make use of the sources in the shared_files folder, you could configure a linked folder such that the alternate location is a new variable whose value is ${PROJECT_LOC}/../shared_files. To add the variable, on the New Folder dialog box, click Advanced and then the click Variables.
Editing a remote linked folder [1]
You can modify the remote location that a remote linked folder points to:
- Right-click the remote linked folder, and then click
Edit Remote Linked Folder.
The Edit Remote Linked Folder dialog box opens.
- The
Containing project and
Folder name fields are both greyed out and cannot be modified. To modify the
Remote location, click
Browse.
The Browse For Folder dialog box opens.
- Choose or create a new connection and then navigate to the remote location.
- Click OK.
- Click Finish.