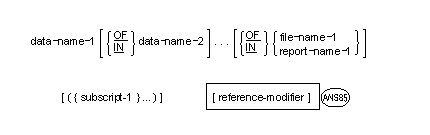
Identifier
An identifier is a sequence of character-strings and separators used to reference data uniquely.
General Formats for Format 1

General Formats for Format 2
General Formats for Format 3
object-property-1
General Formats for Format 4
inline-invocation-1
General Formats for Format 5
identifier-2 object-view-1
General Formats for Format 6
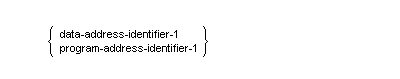
General Formats for Format 7
type-of-identifier-1
Syntax Rules:
- Subscript-1 represents either subscripting (see the section Subscripting) or indexing (see the section Indexing).
General Rules: for Format 2
- The words IN and OF are equivalent.
- A data-name must neither be subscripted nor indexed when it is being used as an index, or subscript.
- Indexing is not permitted where subscripting is not permitted.
- An index can be modified only by the SET, SEARCH, and PERFORM statements. Data items described by the USAGE IS INDEX clause permit storage of the values associated with index-names as data. Such data items are called index data items.
- Literals used as subscripts must be positive numeric integers. Literals used for relative subscripting and indexing must be unsigned numeric integers.
General Rules: for Format 3
- Object-property-1 is defined by the section Object property
General Rules: for Format 4
- Inline-invocation-1 is defined by the section Inline Method Invocation
General Rules: for Format 5
- Object-view-1 is defined by the section Object-view
General Rules: for Format 6
- Address-identifiers are defined by the section Data-address-identifier and the section Program-address-identifier.
General Rules: for Format 7
- Type-of-1 is defined by the section Type of identifier.