Relationship: Tool Has Input Parameter
The Tool has Input Parameter relationship describes exactly one input parameter of a tool. The reference of the relationship is a property whose property value can be passed as parameter to the tool at run time.
The Parameter From attribute determines where the value of the parameters should be obtained from. There are three ways of determining the origin of parameters:
-
Parameter From = Context
The context includes all property values that are available at the start of the execution of an action, and does not change during the tool sequence. For example, if you execute an action on an element, all the property values of the element, the element list in which it is located and the resources where it is found (such as filter, element) are available. The Properties view at run time is a good way of obtaining an overview of the available property values of a selected resource.
-
Parameter From = Previous_Tool
This setting is intended for the transfer of parameters between tools that are temporarily managed in a parameter memory. No property values from this memory are available to the first tool in a tool sequence. As soon as a tool creates an output, the output properties and their values are available for subsequent tools. In the parameter memory, only one property value is saved for a property. See Relationship: Tool Has Output Parameter for more information.
A tool that outputs a property value for a property that already exists in the memory replaces this value, see the figure below.
-
Parameter From = User_Input
User_Input means that the parameter should be entered by the user during the execution of the tool. This is used in tools with a user interface, such as the Input dialog box. In this case, parameter value is transferred to the tool.
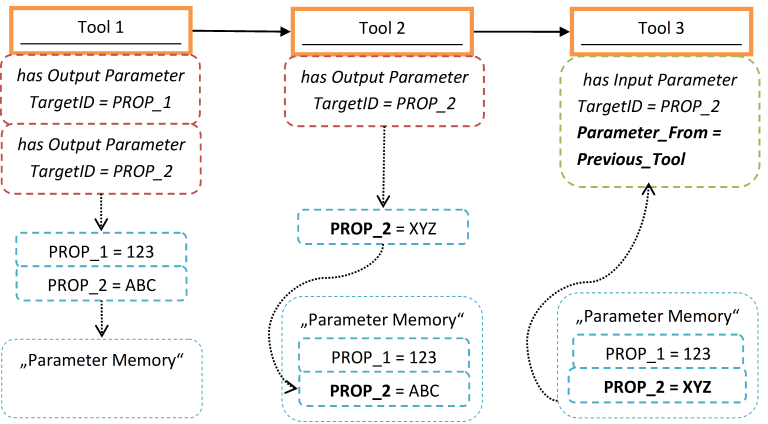
The Parameter Memory is the temporary storage area for output tool parameters. The values 123, ABC and XYZ are the concrete outputs of the respective tools and are saved as property values. The illustration shows how the property PROP_2 has been referenced for two tools as an output parameter. The second output (XYZ) overwrites the first (ABC).
| Attribute | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| TargetIDFile[D] | File Descriptor | Reference to a file descriptor. Only important if the type attribute has been set to File. |
| TargetIDParm[D] | Property | Reference to a property. Only important if the type attribute has been set to Mass Processing or String. |
| DefaultValue [O] | String
(multi line) |
The standard value of the parameter. This value is only used if no other property value can be found for the referenced property.
Has no meaning for file parameters. Initializes a field in an Input dialog box. |
| Label [O] | String | Label of the parameter in dialog boxes. |
| Parameter From | Selection | Determines from where the property value of the parameter property should be obtained.
Valid values include:
|
| SeqNo * [U] | Integer | Position of the parameter. Depending on the tool type, this can be important for the correct execution of the tool. In dialogs, the sequence numbers are used to position the dialog box fields. |
| StaticValue [O] | String
(multi line) |
Sets a fixed value for the parameter. This can only be overwritten via parameter override. See Parameter Override for more information. |
| Type | Selection | The type of the parameter. A property or a file descriptor must be referenced on the basis of this attribute.
Valid values include:
The default value is String. |
| Ui Category [O] | String | Categorizes the parameter in dialogs. Categorized parameters are enclosed in a labeled frame. Successive parameters with the same category are enclosed by the same frame and ordered by sequence number. See The "UI Category" Attribute for more information. |
| Ui Tab [O] | String | Allows the assignment of parameters to tabs. Tabs are individual dialog pages which are activated by clicking the tab label at the top of the dialog. Successive parameters with the same tab are displayed in the same tab page. This works only for Input dialog boxes. See The "UI Category" Attribute for more information. |
| Ui Editable | Boolean | Indicates whether the parameter can be edited in input dialog boxes. Fields are never editable in an output dialog box.
The default value is true. |
| Ui GenericAllowed | Boolean | Indicates whether wildcard characters are permitted as user input. If false, the input dialog box cannot be confirmed if
wildcard characters are present in the input field. See
Application Options for more information.
The default value is false. |
| Ui Mandatory | Boolean | Indicates whether the field is mandatory in Input dialog boxes. If true, the dialog box cannot be confirmed when the field
contains no values.
Mandatory fields are marked with an asterisk *. The default value is true. |
| Ui Form [O] | String | Specifies formatting information for the field in Input dialog boxes. Valid values include: BOLD, HIDDEN, RED, GREEN, YELLOW, BLUE, GRAY. |
| Ui HelpText [O] | String
(multi line) |
Specifies help text for the field in input dialog boxes which is displayed when the question mark button beside the field is clicked or the F1 key is clicked in the field. Clicking in the input field of the attribute opens a dialog box where the help text can be entered in a formatted way. |
| Ui MultiSelection | Boolean | Specifies whether multiple items can be selected. For structured file input parameters only. If set to true, a check box
table is created.
The default value is false. |
| Ui ToolTip [O] | String
(multi line) |
Specifies a tool tip for the field in Input dialog boxes. |
| Visible Condition [O] | Visible_Condition |
This complex attribute is only relevant for a modeled dialog. It allows you to define rules when the input parameter should be shown in the dialog. See Enabled/Visible Condition for details of how to define an enabled or visible condition. |
| Enabled Condition [O] | Enabled_Condition | This complex attribute is only relevant for a modeled dialog. It allows you to define rules when the input parameter should be enabled in the dialog. See Enabled/Visible Condition for details of how to define an enabled or visible condition. |
Examples
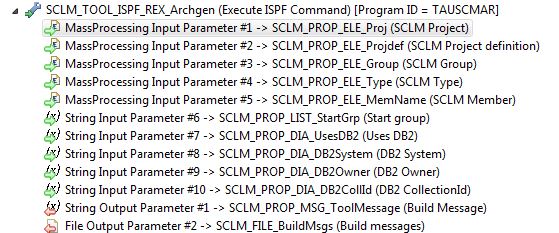
The SCLM Architecture Definition Generation tool (SCLM_TOOL_ISPF_REX_Archgen) is an example of a tool with two different kind of input parameters:
The MassProcessing input parameters are taken from the context in which the action is executed (Parameter From = Context). This means that for each selected item the values of the properties related to the MassProcessing parameters are passed to the tool. In this case, the MassProcessing input parameters are passed to an ISPF REXX tool via the ISPF table TAUTOTIP. The MassProcessing properties of type Parameter From=Context must be available in the context of the selected elements. It is also possible to define all MassProcessing input parameters of type Parameter From=Previous Tool. In this case a preceding tool in the action must supply the MassProcessing input parameters as MassProcessing output parameters. The MassProcessing input parameters of a tool have to come from one source, either the context or from a previous tool.
The String input parameters are taken from the previous tool (Parameter From = Previous_Tool). The values of these properties passed to the tool are identical for each selected element. In this case, the parameters are passed as regular arguments to the ISPF REXX tool. The assumption is that another tool is configured for an action using a preceding tool's parameters. The preceding tool could be an input dialog as in the standard SCLM model or just a tool deriving the String input parameters from some default settings.

The tool SCLM_TOOL_AWM_UI_InputArchgenOptions is of type 'Open Modeled Dialog'. A tool of type 'Open Modeled Dialog' typically has String input parameters which are represented in the dialog as dialog fields. This is where the parameter attributes listed under UI are of relevance. The parameter SCLM_PROP_LIST_StartGrp is derived from the context, the other parameters are taken from user input. A parameter derived from the context presents the value of the dialog field with the current value from the context. Typically, parameters which are mapped to an element type are derived from the context when opening a modeled dialog. Parameters which are not mapped to any element type should be modeled as Parameter From=User_Input in a tool of type 'Open Modeled Dialog'. A tool of type 'Open Modeled Dialog' treats input parameters as output parameters. This means the values entered in the input dialog can be used by following tools in the same action as input parameters with Parameter From=Previous_Tool.

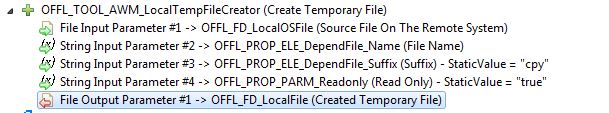
The OFFL_TOOL_AWM_BrowseOSFile tool is an example of a tool which gets a file as an input parameter. Typically, a file input parameter has a Parameter From=Previous_Tool. The file is returned by a preceding tool and is used as an input parameter for the OFFL_TOOL_AWM_BrowseOSFile tool. In the standard SCLM model the previous tool is the tool OFFL_TOOL_AWM_LocalTempFileCreator: