The PROCEDURE DIVISION Header
General Formats for Format 1
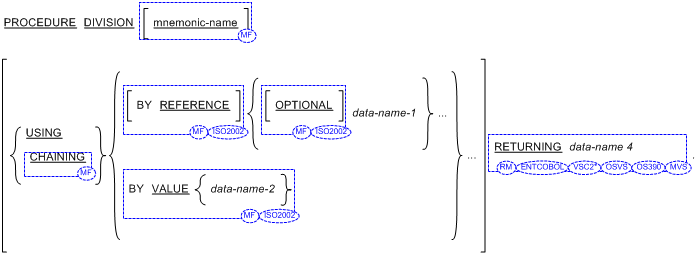
General Formats for Format 2

General Formats for Format 3

Directives
- In addition to Compiler directives which provide flagging and modify the reserved word list, the following directives may
impact either the syntax or the semantics described in this section.
- DEFAULTCALLS - sets the default calling convention if none is explicitly coded in the Procedure Division header.
- STICKY-LINKAGE - controls whether addressability to Linkage Section items is maintained between calls to different entry points in the same program.
Syntax Rules for All Formats
- Mnemonic-name is necessary only if the runtime element is being invoked by another runtime element and that runtime element
is using a calling convention other than that used as default by your COBOL system. Typically, the default COBOL calling convention
is consistent with that used by a significant implementation of a non-COBOL language for the run-time environment.
Mnemonic-name must be defined in the Special-Names paragraph. See the topic The Special-Names Paragraph in the chapter Environment Division for details of how to do this and your COBOL system documentation on interfacing for details of which calling conventions are supported in your run time environment.
- CHAINING and USING are equivalent.
- If data-name-1 or data-name-2 is defined with the USAGE OBJECT REFERENCE clause, the ACTIVE-CLASS phrase must not be specified.
- Data-name-3 must be defined as a level 01 or level 77 entry in the Linkage Section. The data description entry for data-name-3 must not contain a REDEFINES clause. A data item elsewhere in the Linkage Section may specify REDEFINES data-name-3.
- Data-name-3 must not be the same as data-name-1 or data-name-2.
Syntax Rules for Format 1
- Data-name-1 must be defined as a level 01 or a level 77 entry in the Linkage Section
 , File Section or Working-Storage Section
, File Section or Working-Storage Section
. A particular user-defined word must not appear more than once as data-name-1.
It may appear more than once.
The data description entry for data-name-1 must not contain a REDEFINES clause.
It may contain a REDEFINES clause.
Data-name-1 may, however, be the object of a REDEFINES clause elsewhere in the Linkage Section.
- Data-name-2 must be defined as a level 01 or a level 77 entry in the Linkage Section
 , File Section or Working-Storage Section , unless the source unit is a method definition or method prototype definition
, File Section or Working-Storage Section , unless the source unit is a method definition or method prototype definition
. Data-name-2 must be defined as a data item of class numeric, object or pointer.
Data-name-2 can be of any class, but the length must be no greater than 8 bytes.
Syntax Rules for Formats 1 and 3
- The RETURNING phrase must be specified in a function definition and in a function prototype definition.
- The RETURNING phrase may be specified in a method definition, a program definition or a program prototype.
Syntax Rules for Format 2
- Format 2 can only be used in a program in which the EXTERNAL clause is specified in the Program-ID paragraph, that is a call prototype.
- Data-name-1 and data-name-2 must be defined as 01 level records in the Linkage Section.
- Typedef-name-1, typedef-name-2, and typedef-name-3 must be previously defined in the same source file as a programmer-defined usage by means of a TYPEDEF clause.
Syntax Rules for Format 3
- Data-name-1, data-name-2, data-name-4 and data-name-5 must either be defined as 01 level records in the Linkage Section or be followed by the AS phrase.
- Type-name-1 must be a .NET native type.
- Custom-attribute-clause is as decribed in the section The CUSTOM-ATTRIBUTE clause in the Data Division chapter.
- YIELDING may be specified only in the context of an Iterator. See Iterator-ID.
- The type of the item specified in the YIELDING phrase determines the type of the iterator.
General Rules for All Formats
- Up to five data-names are permitted in the USING phrase.
Up to sixty-two data-names are permitted in the USING phrase.
- The BY REFERENCE, the BY VALUE and the BY OUTPUT phrases are transitive across the parameters that follow them until another BY REFERENCE, BY VALUE or BY OUTPUT phrase is encountered. If neither the BY REFERENCE, the BY VALUE nor the BY OUTPUT phrase is specified prior to the first parameter, the BY REFERENCE phrase is assumed.
General Rules for Format 1
- Mnemonic-name identifies the calling convention that this program assumes has been adopted by the calling program that invokes it. This calling convention is also used for subsequent entry points unless those entry points specify a calling convention explicitly. If the calling convention actually used is different to that implied by mnemonic-name, then the COBOL system may become corrupt.
- If data-name-1 is defined as a level 01 or a level 77 entry in the File Section or Working-Storage Section then the activated runtime element operates as if a data item had been declared in the Linkage Section with the same data declaration as data-name-1 and the contents of that data item were moved to data-name-1 prior to executing the first statement in the activated runtime element. In an initial program, these values are overwritten by the initialization of the program's working storage data and are therefore not available to the called program.
- If the activating runtime element is COBOL the following rules apply. If the activating runtime element is not COBOL, see your COBOL system documentation on interfacing for details of when you need to use the BY REFERENCE or BY VALUE clauses.
- At all times in the activated element, references to data-name-1

 , data-name-2 and data-name-3
, data-name-2 and data-name-3
are resolved in accordance with their description in the Linkage Section. If this description defines a greater number of character positions than the corresponding data item in the activating element, unpredictable results can occur. Failure to comply with this rule or exceeding the maximum allowed size of the system area for a particular run time environment may result in the system becoming catastrophically corrupt.
- When a program is called and a BY REFERENCE operand in the USING phrase corresponds to a parameter in the calling program, a referential connection is established and endures until control is returned to the calling program. If the program is called a second time, without any intervening cancel of the program, and that same BY REFERENCE operand does not correspond to a parameter in the calling program, then you must not reference that operand unless the STICKY-LINKAGE Compiler directive is specified.
- data-name 4 must be defined in the Linkage Section.
General Rules for Formats 1 and 3
- The USING phrase identifies the names of the formal parameters used by the program,
 , function
, function

 or method for any arguments passed to it
or method for any arguments passed to it
. The arguments passed to it are identified in the activating source element by one of the following:
- The USING phrase of a CALL statement
- The arguments in a function-identifier
- The USING phrase of an INVOKE statement
- The arguments specified in an inline invocation of a method
- The arguments defined by the rules of an object-property for invocation of an implicit SET property method.
The correspondence between the two lists of names is established on a positional basis
- If the argument is passed by content, the activated runtime element operates as if the record in the Linkage Section were
allocated by the activating runtime element during the process of initiating the activation and as if this record does not
occupy the same storage area as the argument in the activating runtime element.

 If the activated runtime element is a program for which there is no program-specifier in the Repository paragraph of the activating
runtime element, the allocated record is handled as follows.
If the activated runtime element is a program for which there is no program-specifier in the Repository paragraph of the activating
runtime element, the allocated record is handled as follows.
The allocated record is of the same length as the argument, where the maximum length is used if the argument is described as a variable-occurrence data item. That argument is moved to this allocated record without conversion. This record is then treated by the activated runtime element as if it were the argument and as if it were passed by reference.
If the activated runtime element is one of the following:
- A program for which there is a program-specifier in the Repository paragraph of the activating runtime element
- A method
- A function
then this allocated record is one of:
- A data item of the same category, usage, and length as the argument, if the formal parameter is described with the ANY LENGTH clause
- A data item with the same description and the same number of bytes as the formal parameter, where the maximum length is used if the formal parameter is described as a variable-occurrence data item.
The argument is used as the sending operand and the allocated record as the receiving operand in one of the following:
- If the formal parameter is numeric, a COMPUTE statement without the ROUNDED phrase
- If the formal parameter is of class index, object, or pointer, a SET statement
- A MOVE statement.
The allocated record is then treated as if it were the argument and it were passed by reference.
- If the argument is passed by reference, the activated runtime element operates as if the formal parameter occupies the same storage area as the argument.
- If the argument is passed by value, the activated runtime element operates as if the record in the Linkage Section were allocated by the activating runtime element during the process of initiating the activation and as if this record does not occupy the same storage area as the argument in the activating runtime element. This allocated record is exactly the same number of alphanumeric character positions in length as the argument. That argument is moved to this allocated record without conversion. This record is then treated by the activated runtime element as if it were the argument and as if it were passed by reference.
- If the OPTIONAL phrase is specified for data-name-1, you can either specify a valid corresponding argument, or replace the
corresponding argument with the OMITTED phrase; if data-name-1 is not specified as OPTIONAL, you cannot use the OMITTED phrase
as the corresponding argument.
Note that, in COBOL, the storage for the returning item is allocated in the activating source unit. The activated element contains only a formal description in its linkage section.
General Rules for Format 2
- If a call prototype (program with the EXTERNAL clause in the Program-ID paragraph) contains a format 2 PROCEDURE DIVISION
header and another program in the same source file includes a CALL literal statement referencing the program-name of this
call prototype, then the following rules apply:
- If a call convention is specified in the CALL statement, it must match that specified (implicitly or explicitly) in the prototype. If no call convention is specified in the CALL statement, the call convention specified (implicitly or explicitly) in the prototype is used.
- The number of parameters specified in the CALL statement must equal the number of parameters specified in the prototype, except as allowed by the REPEATED phrase.
- For each parameter specified in the CALL statement, the following rules apply:
- If there is a BY REFERENCE or a BY CONTENT phrase associated with the parameter, the corresponding parameter in the prototype must be specified BY REFERENCE.
- If there is a BY VALUE phrase associated with the parameter, the corresponding parameter in the prototype must be specified BY VALUE.
- If the parameter in the CALL statement has no BY REFERENCE, BY CONTENT or BY VALUE phrase, the phrase specified (implicitly or explicitly) in the prototype is used.
- This rule overrides the rules that apply when no matching call prototype is found. In other words, when no call prototype is used, all parameters up to the first BY phrase are treated as if BY REFERENCE were specified and all parameters after any BY phrase, that do not themselves have an explicit BY phrase, use the last one in effect. However, when a matching call prototype is found, its definitions for the BY phrases take precedence.
- If the parameter in the prototype is of class numeric, or it is a pointer or index data-item, then the parameter in the CALL must have the same data definition.
- If the parameter in the prototype is of class alphanumeric, the parameter in the CALL must also be of class alphanumeric and be at least as long as the parameter in the prototype.
- If ANY is specified in the prototype, the parameter in the CALL statement can be of any class.
- If the CALL statement includes the GIVING or RETURNING clause, the prototype must also include the clause, and vice versa. The data definition of the data item specified in the CALL must be the same as that of the data item specified in the prototype.
- The DELIMITED BY SIZE phrase in the prototype can be used only for alphanumeric parameters. In this case, the corresponding parameter in the CALL statement is moved to an implicitly allocated data area, and a binary 0 (x"00") character is placed immediately following this copy of the data. If the BY SIZE phrase is omitted, the corresponding parameter in the CALL statement is moved to an implicitly allocated data area, and a binary 0 (x"00") character is placed immediately following the last non-space character in the copy data. The intention is to help in interfacing to languages such as C, which use null terminated text strings.
- The REPEATED phrase indicates that there must be at least integer-1 and no more than integer-2 repetitions of the final parameter. If integer-1 TO integer-2 is not specified, integer-1 is taken as 0 and integer-2 as infinite.
General Rules for Format 3
- The data item referenced by data-name-5 has no value when the runtime element is activated. An attempt to access the value of the data item referenced by data-name-5 prior to that item being a receiving item will result in a runtime exception..
- At all times in the activated element, references to data-name-1, data-name-2, data-name-4 and data-name-5 are resolved in accordance with their description in the Linkage Section or the AS phrase. If this description defines a greater number of character positions than the corresponding data item in the activating element, unpredictable results can occur. Failure to comply with this rule or exceeding the maximum allowed size of the system area for a particular run time environment may result in the system becoming catastrophically corrupt.
- If the CUSTOM-ATTRIBUTE clause is specified, the custom attribute information is included in the generated code..