The principal purpose of an AccuRev workspace is to provide an isolated location for performing development tasks. The changes you make do not affect your colleagues until you decide to make them public, using the Promote command. Likewise, the changes that others make do not immediately affect your workspace. You must execute an Update command to bring versions created (and then promoted) by your colleagues into your workspace.
You invoke the Update command in the File Browser, using the File > Update command or a button above the Workspace Explorer.
During execution of the Update command, a progress window appears (See “The Update Progress Box”.). A user preference controls how this window is used.) See “AccuRev Preferences (Tools > Preferences Command)”.
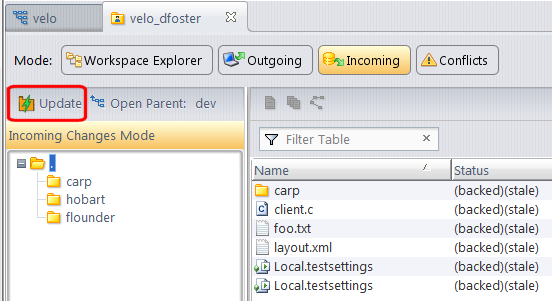
Tip: Prior to executing the Update command, use Incoming Changes mode ( ) to see what the Update will do. See Incoming Changes Mode for more information.
) to see what the Update will do. See Incoming Changes Mode for more information.
At its simplest, an update just copies versions of some file elements from your workspace's backing stream into the workspace. For example, your colleagues may have edited the contents of files colors.java and main_menu.java, created new versions of them in their workspaces, then promoted the versions to the common backing stream. When you invoke Update, the new versions of those two files are copied from the depot to your workspace, overwriting the older versions of the file.
In addition to incorporating such content changes into your workspace, Update incorporates namespace changes:
|
•
|
defuncting of existing files and directories
|
AccuRev tracks namespace changes in the same way as content changes -- by saving each change as a new version in your workspace. If you Rename file colors.java to colours.java, the change is recorded as a new version of the file. Changing the name again, to hues.java, creates another new version.
Similarly, defuncting file rgb.java creates a new version of the file in your workspace.
The following sections provide an overview of how Update works.
The basic Update strategy is to leave the files you're working on undisturbed, and to copy any new versions of other files into the workspace. This enables the workspace to provide the safety of isolation, while still "keeping in touch" with other users' progress.
Roughly speaking, Update partitions the files in your workspace tree into two categories, to determine which are candidates for updating:
|
•
|
Files that you're currently working on. AccuRev uses the concept of default group to keep track of the files you're working on. Files are placed in the default group when you process them with such AccuRev commands as Send to Workspace, Keep, and Rename. These files are not candidates for updating, because it would overwrite your changes.
|
|
•
|
All the other files. The files that you're not currently working on are candidates for updating. AccuRev will update all such files for which a more recent version exists in the backing stream.
|
But things are not quite this simple. You might have edited other files, too, without preserving the changes with the Keep command. Such files have (modified) status.
In many cases, no one else has been working on those files. If no new versions of the (modified)-status files have been created in the backing stream since your most recent Update, the update proceeds, leaving those files alone.
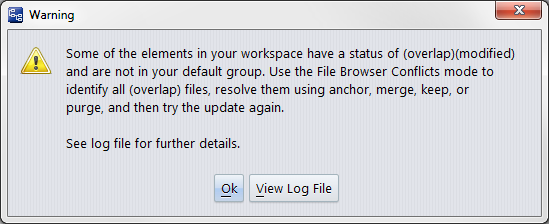
But suppose one or more of the files does have a new version in the backing stream. In this case, the file's status is (modified)(overlap). Update won't simply overwrite the file with the backing-stream version, but it can attempt to merge the file with the backing-stream version:
|
•
|
Unless you have set the Update Resolves Trivial Merges user preference, AccuRev displays a warning message like this:
 |
|
•
|
If user preference Update Resolves Trivial Merges is selected, Update determines whether a merge can be performed automatically on all files with (modified)(overlap) status. If so, the update proceeds. If not, the update terminates with an error box:
 |
AccuRev documentation often uses the term active to describe the elements that are members of the default group.
To improve performance, the Timestamp Optimization algorithm and ignore patterns enable Update to avoid examining every file in the workspace tree. (See the AccuRev Administrator’s Guide for more information on these topics.)
By default, AccuRev allows you to edit any file in a workspace at any time -- it doesn't require you to perform a "check out" operation on a file before editing it. This provides convenience and flexibility, but the edited files (with "non-member" status) can abort an Update. You can use the anchor-required workspace and/or exclusive file locking feature to ensure files never get "non-member" status, thus guaranteeing that Update will always proceed. See “File Locking”.
This step is efficient and speedy. Update needs to consider only the elements that were involved in transactions recorded since the workspace's previous update. Only these transactions can contain changes that have not yet been incorporated into the workspace.
Update next applies both content changes and namespace changes to elements in the workspace:
|
•
|
It applies content changes to file elements by copying the backing-stream versions from the repository to the workspace tree. For (modified)(overlap)-status files, it merges the backing-stream version with the file in the workspace tree.
|
After AccuRev has completed updating versions in the workspace, the workspace is "up to date as of transaction N "; N is the workspace's update level. The higher this value, the fewer transactions your next invocation of Update will need to examine, in order to determine which elements need to be updated.