Developers working on their files is the principal activity in any software development environment. With AccuRev, a developer’s files are stored in an ordinary directory structure — perhaps on the hard drive of a personal computer or laptop, perhaps in a designated area of a well-backed-up disk farm, etc. The only thing special about this “developer’s work area” is that AccuRev keeps track of its association with a particular depot. (The work area is called a workspace — for more information, see AccuRev Workspaces and Reference Trees.)
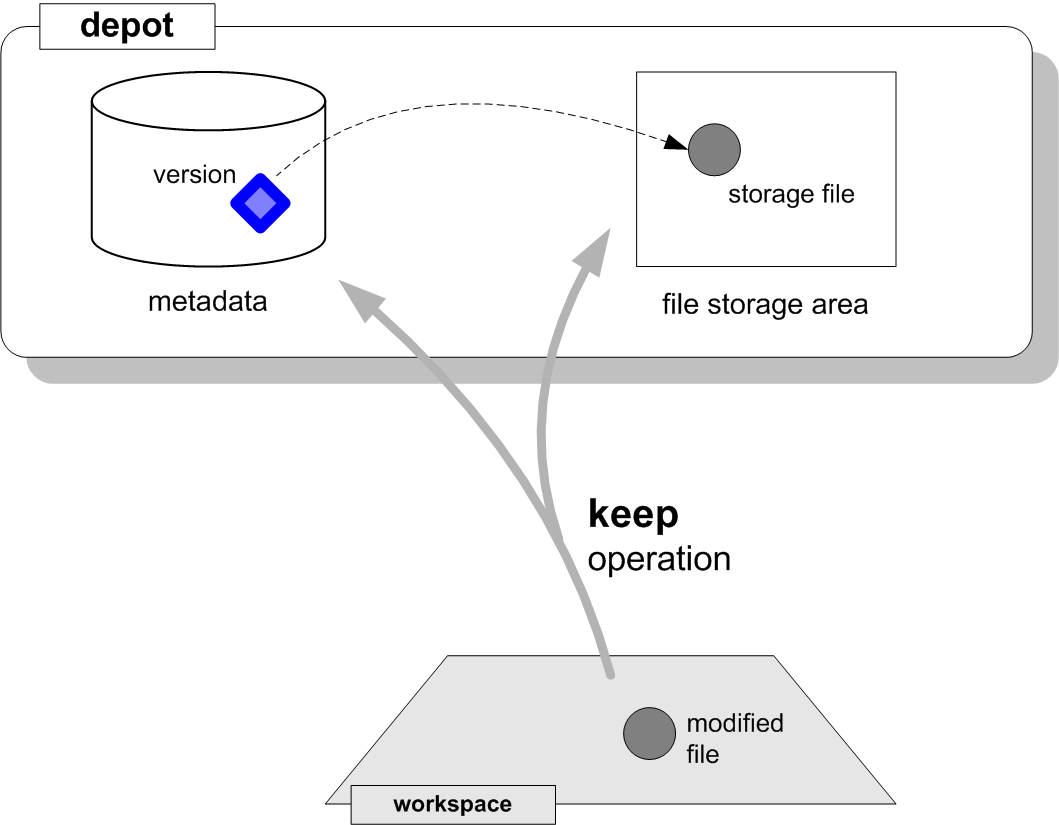
A developer can use any software tools to create and edit files, compile and build modules and applications. AccuRev doesn’t get involved in these operations at all, so there’s no performance penalty. Every so often, the developer tells AccuRev to save the current contents of a file (or a group of files) to the depot’s repository. This operation, called a keep, does two things:
|
•
|
Copies the current contents of the file to a container file in the depot’s file storage area.
|
|
•
|
Creates an associated version object in the depot’s schema.
|
In all modern operating systems, files are organized into directories (or folders). Some operating systems also support additional kinds of file system objects: symbolic links, hard links, device files, named pipes, etc.
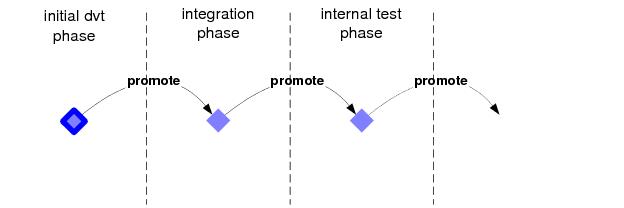
Software development is much more than just creating and modifying files. A typical development project involves many phases, possibly including initial development, integration of work done independently, internal system testing, external testing, and final production. AccuRev uses a “promotion model” to manage files in these multiple development phases. Files progress through the phases, one by one: when a set of files pass the tests (if any) mandated for a particular phase, a user working on that phase promotes them to the next phase.
AccuRev distinguishes between the original version, created by a keep operation, and all the additional versions created by a promote operation:
|
•
|
A real version is created by operations like keep, add, merge, rename, etc. The operation creates a new version object in the metadata stored for the depot and places a new file in the depot’s file storage area.
|
|
•
|
A virtual version is created by a promote. It creates a new version object in the metadata stored for the depot, which provides an additional reference to an existing file in the file storage area. Conversely, a demote operation removes a virtual version.
|