Domain-Based Multi-Homing
Domain-based multi-homing is based on the cookie domain. For example, if you have a cookie domain company.com, you can prefix hostnames to a cookie domain name. For a test resource, you can prefix test to company.com and have test.company.com resolve to the IP address of Access Gateway. Access Gateway configuration for the test.company.com proxy service contains the information for accessing its web servers (test1.com).
Figure 2-16 Using a Base Domain Name with Host Names
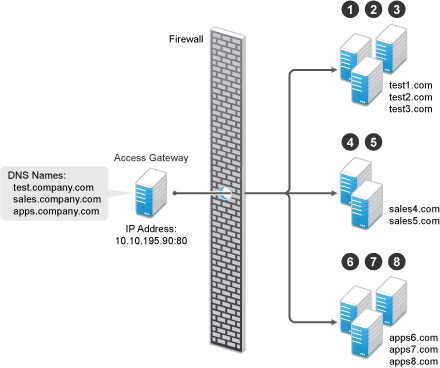
Domain-based multi-homing has the following characteristics If you are using SSL:
-
Back-end servers can all listen on the same SSL port (the default for HTTPS is 443).
-
Back-end servers can share the same SSL certificate. Instead of using a specific hostname in the SSL certificate, the certificate can use a wildcard name such as *.company.com, which matches all the servers.
Before configuring Access Gateway, you need to complete the following:
-
Create the published DNS names with a common domain name for public access to the back-end resources. For example, the table below lists three DNS names that use company.com as a common domain name, lists the IP address that these DNS names resolve to, and the web servers they protect.
Published DNS Name
Access Gateway IP Address
Web Server Host Name
Web Server IP Address
test.company.com
10.10.195.90:80
test.internal.com
10.10.15.10
sales.company.com
10.10.195.90:80
sales.internal.com
10.10.15.20
apps.company.com
10.10.195.90:80
apps.internal.com
10.10.15.30
-
Configure your DNS server to resolve the published DNS names to the IP address of Access Gateway.
-
Set up the back-end web servers.
-
Create three proxy services for these published DNS names.
To create a domain-based multi-homing proxy service, see Creating a Second Proxy Service, and select domain-based for the multi-homing type.